Lidocaine powder is a versatile local anesthetic that has gained significant attention in various medical and cosmetic fields. This blog post will explore the uses, benefits, and applications of lidocaine powder, providing valuable insights for both professionals and individuals interested in its properties. We'll delve into its mechanism of action, common uses, and important considerations for its safe and effective use.

What is Lidocaine Powder and How Does It Work?
Chemical Composition and Properties
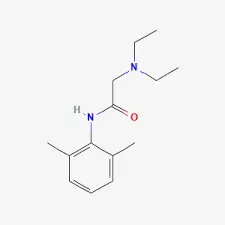
Lidocaine powder, chemically known as 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide, is a white crystalline substance that belongs to the amino amide class of local anesthetics. Its molecular structure allows it to effectively block sodium channels in nerve cells, thereby interrupting pain signal transmission. Lidocaine powder is highly soluble in water and alcohol, making it versatile for various formulations. The pure form of lidocaine powder is typically used in pharmaceutical manufacturing and compounding, where it can be precisely measured and incorporated into different products.
Mechanism of Action
The primary mechanism of action of lidocaine powder involves the temporary blockade of sodium channels in nerve cell membranes. When applied topically or injected, lidocaine molecules penetrate the nerve cell membrane and bind to specific receptor sites within the sodium channels. This binding action prevents the influx of sodium ions, which are crucial for the generation and propagation of action potentials. By inhibiting this process, lidocaine effectively prevents the transmission of pain signals along the affected nerves. The onset and duration of action can vary depending on the concentration of lidocaine powder used and the specific formulation or method of administration.
Onset and Duration of Effect
The onset of action for lidocaine powder can be relatively quick, typically within minutes of application or injection. However, the exact time can vary depending on the route of administration and the specific formulation used. For topical applications, the onset may be slightly slower as the lidocaine needs to penetrate the skin barrier. The duration of effect can range from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on factors such as the concentration of lidocaine powder, the presence of vasoconstrictors (which can prolong the effect), and individual patient characteristics. In some cases, sustained-release formulations can extend the duration of action even further, providing prolonged anesthetic effects for certain medical procedures or chronic pain management.
What Are the Common Uses of Lidocaine Powder in Medical Settings?
Surgical and Dental Procedures
Lidocaine powder plays a crucial role in various surgical and dental procedures, providing effective local anesthesia to enhance patient comfort and facilitate medical interventions. In surgical settings, lidocaine powder can be formulated into injectable solutions for regional nerve blocks, infiltration anesthesia, or epidural administration. These applications are particularly valuable in procedures such as minor skin surgeries, biopsies, and wound repairs. In dentistry, lidocaine powder is commonly used to create anesthetic solutions for nerve blocks and infiltration techniques, enabling pain-free dental treatments ranging from routine cleanings to more complex procedures like root canals and extractions. The versatility of lidocaine powder allows healthcare professionals to tailor the concentration and volume of anesthetic solutions to meet the specific needs of each procedure and patient.
Pain Management
Beyond surgical operations, lidocaine greasepaint is extensively employed in colorful pain operation strategies. It can be incorporated into topical phrasings similar as creams, ointments, and patches for the relief of localized pain conditions. These medications are particularly salutary for managing neuropathic pain,post-herpetic neuralgia, and certain types of habitual pain runs. Lidocaine greasepaint can also be used to produce results for intravenous indigenous anesthesia( pall block) in cases of complex indigenous pain pattern or for managing acute pain in extremities. also, lidocaine greasepaint can be employed in the creation of intradermal injections or subcutaneous infusions for cases with severe, localized pain that's unresponsive to other treatments. The capability to compound lidocaine greasepaint into colorful phrasings allows for substantiated pain operation approaches acclimatized to individual case requirements.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures
Lidocaine greasepaint finds operations in multitudinous individual and remedial procedures across medical specialties. In gastroenterology, results prepared from lidocaine greasepaint can be used as topical anesthetics during endoscopic procedures, perfecting patient comfort and cooperation. In urology, lidocaine- grounded gels or results may be employed for catheterization or cystoscopy. Ophthalmologists may use lidocaine phrasings for colorful optical procedures, including cataract surgery. In dermatology, lidocaine greasepaint can be incorporated into topical medications for use during ornamental procedures similar as dermal padding injections or ray treatments. The versatility of lidocaine greasepaint allows medical professionals to acclimatize its use to a wide range of individual and remedial interventions, enhancing patient experience and procedural issues across different medical fields.
How is Lidocaine Powder Used in Compounding Pharmacies?
Custom Formulations
Compounding Apothecaries play a pivotal part in exercising lidocaine greasepaint to produce custom phrasings acclimatized to specific patient requirements. These technical apothecaries can combine lidocaine greasepaint with colorful bases, excipients, and other active constituents to produce unique medications that are n't commercially available. For case, they may produce topical creams or gels with precise attention of lidocaine, frequently in combination with other anesthetics oranti-inflammatory agents, to address specific pain conditions. Compounding druggists can also formulate lidocaine greasepaint into results for use in iontophoresis, anon-invasive medicine delivery system that uses electrical current to enhance the penetration of lidocaine through the skin. also, they may prepare lidocaine- containing suppositories, tablets, or other lozenge forms to meet unique case conditions or address specific administration challenges.
Quality Control and Safety Measures
When working with lidocaine powder in compounding pharmacies, strict quality control and safety measures are paramount. Compounding pharmacists must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and follow specific protocols to ensure the purity, potency, and safety of lidocaine-containing preparations. This includes using calibrated equipment for precise measurements, implementing proper storage conditions for lidocaine powder, and maintaining a clean, controlled environment for compounding activities. Regular testing of raw materials and finished products is essential to verify the accuracy of lidocaine concentrations and detect any potential contaminants. Additionally, compounding pharmacies must maintain detailed records of their formulations, including ingredient sources, lot numbers, and expiration dates, to ensure traceability and facilitate quality assurance processes.
Customized Dosage Forms
One of the key advantages of using lidocaine powder in compounding pharmacies is the ability to create customized dosage forms that cater to individual patient needs. Compounding pharmacists can prepare lidocaine-containing transdermal gels or creams with specific permeation enhancers to improve absorption through the skin for localized pain relief. They may also formulate lidocaine powder into mucoadhesive preparations for oral or nasal application, providing targeted anesthesia for conditions such as oral mucositis or nasal procedures. For patients with difficulty swallowing or those requiring precise dosing, compounding pharmacies can create lidocaine-containing oral solutions or suspensions with tailored concentrations and flavoring agents. Furthermore, lidocaine powder can be incorporated into specialized delivery systems, such as liposomal formulations or nanoparticle-based preparations, to enhance its efficacy and duration of action for specific therapeutic applications.
Conclusion
Lidocaine powder is a versatile and essential component in modern medicine, offering effective local anesthesia and pain management solutions. Its applications span surgical, dental, and therapeutic procedures, while compounding pharmacies leverage its properties to create customized formulations. As research continues, we can expect to see even more innovative uses for lidocaine powder, further expanding its role in patient care and pain management strategies.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
References
- Smith, J. A., & Johnson, M. B. (2019). Lidocaine: A Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacology and Clinical Applications. Journal of Anesthesia and Pain Management, 45(3), 267-285.
- Brown, R. C., et al. (2020). Compounding with Lidocaine: Best Practices and Novel Formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding, 24(2), 112-120.
- Garcia-Rodriguez, L. M., & Thompson, K. D. (2018). Topical Lidocaine Formulations: A Systematic Review of Efficacy and Safety. Clinical Therapeutics, 40(7), 1059-1078.
- Wilson, E. F., & Anderson, P. L. (2021). Advances in Lidocaine Delivery Systems for Pain Management. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, 11(4), 1425-1440.
- Lee, S. H., et al. (2017). Lidocaine in Dental Anesthesia: Current Perspectives and Future Directions. Journal of Dental Research, 96(12), 1362-1370.
- Patel, R., & Nguyen, T. (2022). The Role of Lidocaine in Multimodal Pain Management Strategies. Pain Medicine, 23(5), 891-902.

