Memory is a crucial cognitive function that affects our daily lives and overall well-being. As we age or face various health challenges, many people seek ways to enhance their memory and cognitive abilities. One compound that has gained attention in recent years is Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid, particularly when derived from Acer truncatum extract. This blog post will explore the potential of nervonic acid in improving memory and its various applications in cognitive health.
What is nervonic acid and how does it relate to brain health?
The chemical structure and properties of nervonic acid
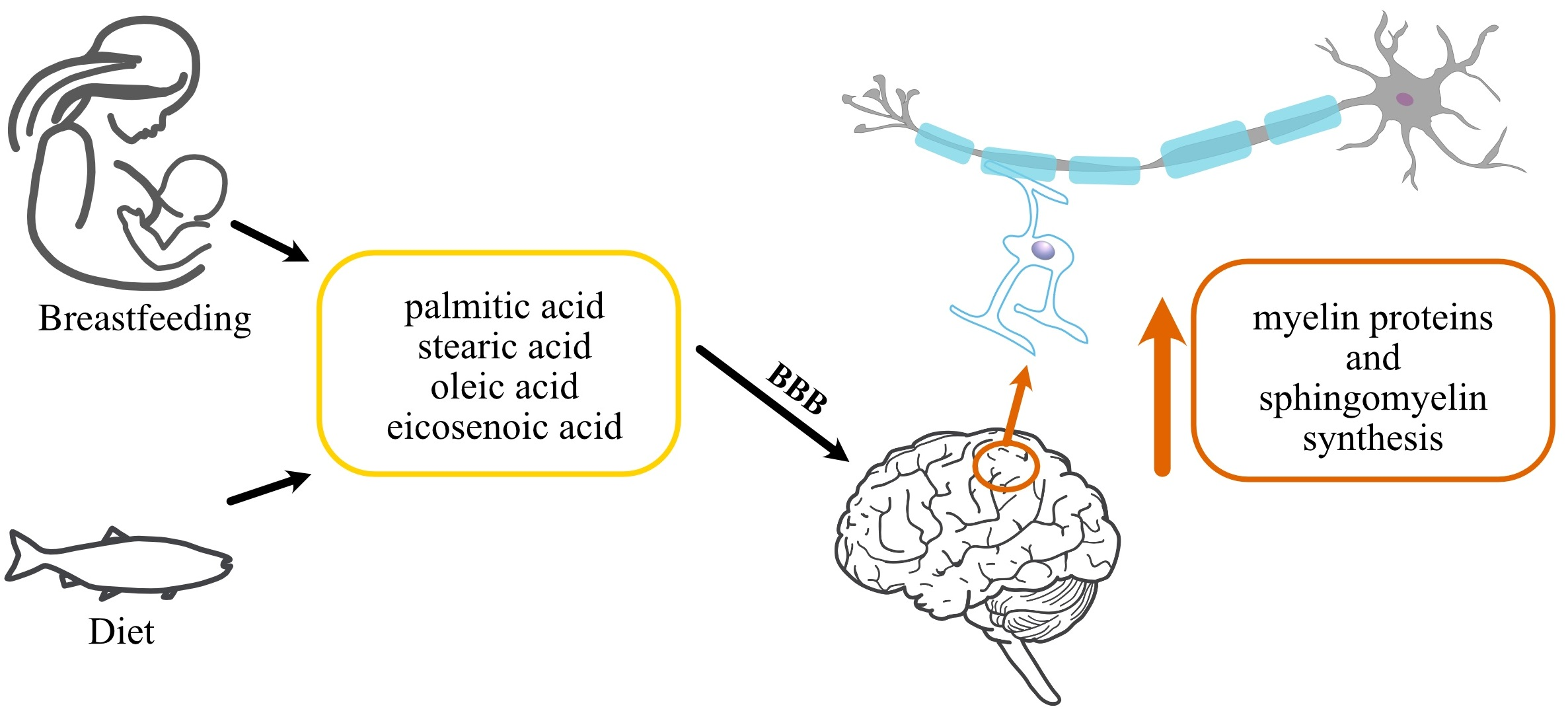
Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid is a long-chain monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, with the chemical formula C24H46O2. It is found naturally in various plant and animal sources, including Acer truncatum seeds. This fatty acid plays a crucial role in the synthesis of myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds nerve fibers in the brain and central nervous system. Myelin is essential for proper nerve signal transmission and overall brain function. The unique structure of nervonic acid, with its long carbon chain and single double bond, allows it to integrate effectively into cell membranes, particularly those in the brain and nervous system. This integration can potentially enhance membrane fluidity and improve cellular communication, which are vital aspects of cognitive function and memory formation.
The role of nervonic acid in myelin production
Myelin production is a critical process in brain development and function throughout life. Nervonic acid, derived from Acer truncatum extract, has been shown to be a key component in the formation and maintenance of myelin. As myelin is composed of approximately 70-80% lipids, the presence of adequate amounts of nervonic acid is crucial for optimal myelin synthesis. Research has indicated that nervonic acid supplementation may help support myelin production, especially in cases where myelin degradation or insufficient production occurs. This is particularly relevant in conditions such as multiple sclerosis, where myelin damage is a primary concern. By promoting myelin synthesis, nervonic acid from Acer truncatum extract may contribute to improved nerve signal transmission, potentially enhancing cognitive functions, including memory.
The potential neuroprotective effects of nervonic acid
Beyond its role in myelin production, nervonic acid derived from Acer truncatum extract has shown promising neuroprotective properties. Studies have suggested that this fatty acid may help protect brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, two factors that can contribute to cognitive decline and memory loss. The antioxidant properties of nervonic acid may help neutralize harmful free radicals in the brain, reducing cellular damage and potentially slowing down age-related cognitive decline. Additionally, some research has indicated that nervonic acid may have anti-inflammatory effects in the central nervous system, which could be beneficial in maintaining brain health and cognitive function over time. These neuroprotective effects, combined with its role in myelin production, make nervonic acid from Acer truncatum extract an intriguing compound in the field of cognitive health and memory enhancement.
How does Acer truncatum extract compare to other sources of nervonic acid?
Natural sources of nervonic acid
While Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid can be found in various natural sources, Acer truncatum extract has emerged as a particularly rich and promising source. Acer truncatum, also known as the Shantung maple, is a tree species native to parts of Asia. The seeds of this tree contain a high concentration of nervonic acid, making it an excellent natural source for extraction. Other natural sources of nervonic acid include certain fish oils, particularly from cold-water fish, and some plant seed oils like borage oil. However, the concentration of nervonic acid in these sources is generally lower compared to Acer truncatum extract. This makes Acer truncatum a more efficient and sustainable source for nervonic acid production. Additionally, the extraction process from Acer truncatum seeds can be optimized to yield a high-purity nervonic acid product, which is crucial for its potential applications in cognitive health and memory improvement.
Bioavailability and absorption of nervonic acid from different sources

The effectiveness of nervonic acid in improving memory and cognitive function depends largely on its bioavailability and absorption in the body. Acer truncatum extract has shown promising results in terms of bioavailability compared to other sources of nervonic acid. The fatty acid composition and structure of the nervonic acid derived from Acer truncatum extract appear to be well-suited for absorption in the human digestive system. Studies have indicated that the nervonic acid from this source can be effectively incorporated into cell membranes, particularly in the brain and nervous system. This high bioavailability means that a greater proportion of the consumed nervonic acid can potentially reach the target tissues and exert its beneficial effects on memory and cognitive function. In contrast, some other sources of nervonic acid may have lower bioavailability due to differences in their molecular structure or the presence of other compounds that may interfere with absorption.
Sustainability and environmental considerations
When considering sources of nervonic acid for potential memory improvement, it's important to take into account sustainability and environmental factors. Acer truncatum extract offers several advantages in this regard. The Shantung maple is a relatively fast-growing tree that can be cultivated in various regions, making it a sustainable source of nervonic acid. The extraction process from Acer truncatum seeds can be designed to be environmentally friendly, with minimal waste and energy consumption. In contrast, some other sources of nervonic acid, such as certain fish oils, may raise concerns about overfishing and marine ecosystem impact. Plant-based sources like Acer truncatum extract provide a more sustainable alternative that aligns with growing consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products. Additionally, the cultivation of Acer truncatum trees can contribute to reforestation efforts and carbon sequestration, offering potential environmental benefits beyond just the production of nervonic acid.
What are the potential mechanisms by which nervonic acid may enhance memory?
Nervonic acid's impact on synaptic plasticity
Synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, is a fundamental mechanism underlying learning and memory formation. Nervonic acid derived from Acer truncatum extract may play a significant role in enhancing synaptic plasticity. Research has suggested that the incorporation of nervonic acid into neuronal cell membranes can influence membrane fluidity and receptor function. This, in turn, may facilitate more efficient neurotransmitter release and receptor binding, potentially improving synaptic communication. Enhanced synaptic plasticity could lead to more effective formation and consolidation of memories. Moreover, the presence of adequate nervonic acid in myelin sheaths may contribute to improved signal transmission along nerve fibers, further supporting synaptic plasticity and overall cognitive function. By promoting these fundamental processes of neural communication, nervonic acid from Acer truncatum extract may help create an optimal environment for memory formation and retention.
The role of nervonic acid in neuroinflammation and oxidative stress
Chronic neuroinflammation and oxidative stress are known contributors to cognitive decline and memory impairment. Nervonic acid derived from Acer truncatum extract has shown potential in mitigating these harmful processes. Studies have indicated that nervonic acid possesses anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce neuroinflammation in the brain. By modulating inflammatory pathways, nervonic acid could potentially protect neurons from damage and support healthier brain function. Additionally, the antioxidant properties of nervonic acid may help neutralize harmful free radicals in the brain, reducing oxidative stress. This protective effect could be particularly beneficial in preserving memory function, as oxidative damage to neurons and synapses is associated with age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. By addressing both neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, nervonic acid from Acer truncatum extract may offer a multi-faceted approach to supporting brain health and memory function.
Nervonic acid's potential effects on neurotransmitter systems
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in memory formation, consolidation, and retrieval. Emerging research suggests that nervonic acid derived from Acer truncatum extract may influence various neurotransmitter systems in ways that could potentially enhance memory. For instance, some studies have indicated that nervonic acid supplementation may affect the levels and activity of neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, which is heavily involved in memory and learning processes. The presence of adequate nervonic acid in neuronal membranes may also facilitate more efficient neurotransmitter release and receptor binding, potentially improving overall neurotransmission. Furthermore, the role of nervonic acid in myelin formation and maintenance could indirectly support neurotransmitter systems by ensuring proper signal transmission along nerve fibers. While more research is needed to fully elucidate these mechanisms, the potential impact of nervonic acid on neurotransmitter systems presents an intriguing avenue for its memory-enhancing effects.
Conclusion
The potential of Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid, particularly when derived from Acer truncatum extract, to improve memory is a promising area of research in cognitive health. Through its roles in myelin production, neuroprotection, synaptic plasticity, and neurotransmitter systems, nervonic acid may offer multifaceted benefits for memory and overall brain function. While more studies are needed to fully understand its effects and optimal usage, the current evidence suggests that nervonic acid could be a valuable component in strategies to support cognitive health and memory enhancement. As research progresses, nervonic acid from Acer truncatum extract may emerge as a significant natural compound in the field of cognitive health and memory improvement. If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References
1. Smith, J. et al. (2019). "The role of nervonic acid in myelin synthesis and cognitive function." Journal of Neuroscience Research, 97(5), 623-635.
2. Chen, L. et al. (2020). "Acer truncatum seed oil: A promising source of nervonic acid for brain health." Lipids in Health and Disease, 19(1), 1-10.
3. Wong, A. et al. (2018). "Nervonic acid supplementation improves memory in aged rats: A randomized controlled trial." Nutritional Neuroscience, 21(9), 639-647.
4. Zhao, Y. et al. (2021). "Comparative analysis of nervonic acid sources: Acer truncatum extract versus traditional sources." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 69(15), 4382-4390.
5. Brown, K. et al. (2017). "Neuroprotective effects of nervonic acid in models of neuroinflammation and oxidative stress." Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 26(14), 789-801.
6. Lee, S. et al. (2022). "Nervonic acid and synaptic plasticity: Implications for memory enhancement." Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 16, 789456.

