Neurodegenerative diseases pose a significant challenge to global health, affecting millions of people worldwide. As researchers continue to explore potential treatments, natural compounds have gained attention for their possible neuroprotective properties. One such compound that has sparked interest is Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid, particularly its component nervonic acid. This blog post will delve into the potential benefits of Acer truncatum extract in addressing neurodegenerative diseases and explore the current scientific understanding of its effects.
What is Acer truncatum extract and how does it relate to nervonic acid?
The origins and composition of Acer truncatum extract
Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid, commonly known as the Shantung maple, is a species of maple tree native to eastern Asia. The extract derived from this tree has gained attention in recent years due to its unique composition of bioactive compounds. Among these compounds, nervonic acid stands out as a particularly interesting component. Acer truncatum extract is rich in nervonic acid, a long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid that plays a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of myelin sheaths in the nervous system. This natural source of nervonic acid has piqued the interest of researchers investigating potential treatments for neurodegenerative diseases, as myelin degradation is a common feature in many of these conditions.

The importance of nervonic acid in brain health
Nervonic acid, a key component of Acer truncatum extract, is essential for maintaining the integrity of the myelin sheath, which insulates and protects nerve fibers. This fatty acid is particularly abundant in the white matter of the brain and is crucial for proper nerve signal transmission. In neurodegenerative diseases, the myelin sheath often deteriorates, leading to impaired neural communication and various neurological symptoms. The presence of nervonic acid in Acer truncatum extract has led researchers to investigate its potential in supporting brain health and possibly mitigating the effects of neurodegenerative diseases. By providing a natural source of this important fatty acid, Acer truncatum extract may offer a promising avenue for supporting myelin health and overall neurological function.
Extraction methods and quality control
The efficacy of Acer truncatum extract in providing nervonic acid depends largely on the extraction methods employed and the quality control measures in place. Various techniques, such as supercritical CO2 extraction and solvent extraction, are used to obtain the extract from Acer truncatum seeds. These methods aim to maximize the yield of nervonic acid while minimizing the presence of unwanted compounds. Quality control is crucial in ensuring the consistency and potency of the extract, as factors like harvesting time, storage conditions, and processing techniques can all affect the nervonic acid content. Standardization of Acer truncatum extract is essential for reliable research outcomes and potential therapeutic applications, particularly when investigating its effects on neurodegenerative diseases. As research in this area progresses, refinements in extraction and quality control methods will likely play a significant role in optimizing the potential benefits of Acer truncatum extract and its nervonic acid content.
How does Acer truncatum extract potentially impact neurodegenerative diseases?
Neuroprotective properties of Acer truncatum extract
Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid, rich in nervonic acid, has shown promising neuroprotective properties that may be beneficial in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have suggested that the extract may help protect neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation, two key factors in the progression of many neurodegenerative conditions. The nervonic acid present in Acer truncatum extract is thought to play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of myelin sheaths, which are often compromised in diseases like multiple sclerosis and certain forms of dementia. By potentially supporting myelin health, the extract may help preserve neural communication and function. Additionally, some research has indicated that Acer truncatum extract may have antioxidant properties, which could further contribute to its neuroprotective effects by neutralizing harmful free radicals in the brain.
Effects on cognitive function and memory
The potential impact of Acer truncatum extract on cognitive function and memory has been a subject of growing interest among researchers. Some studies have suggested that the nervonic acid present in the extract may support cognitive processes by promoting the health of neural pathways. In animal models, administration of Acer truncatum extract has been associated with improvements in spatial memory and learning abilities. These effects are thought to be linked to the extract's role in maintaining myelin integrity, which is crucial for efficient signal transmission between neurons. Furthermore, the neuroprotective properties of Acer truncatum extract may help preserve cognitive function by potentially slowing the progression of neuronal damage associated with neurodegenerative diseases. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms at play, these preliminary findings suggest that Acer truncatum extract and its nervonic acid content may hold promise in supporting cognitive health and potentially mitigating age-related cognitive decline.
Potential mechanisms of action in neurodegenerative diseases
The potential mechanisms by which Acer truncatum extract may influence neurodegenerative diseases are multifaceted and still under investigation. One key mechanism is thought to be related to the extract's high content of nervonic acid, which may support the synthesis and maintenance of myelin. In neurodegenerative conditions where myelin degradation is a prominent feature, such as multiple sclerosis, this could potentially help slow disease progression. Additionally, some studies have suggested that Acer truncatum extract may modulate inflammatory responses in the central nervous system, potentially reducing neuroinflammation associated with various neurodegenerative diseases. The extract's antioxidant properties may also play a role in protecting neurons from oxidative damage, a common factor in many neurodegenerative processes. Furthermore, there is emerging evidence that Acer truncatum extract may influence cellular signaling pathways involved in neuronal survival and plasticity, which could contribute to its neuroprotective effects. As research in this area continues, a more comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms may pave the way for targeted therapeutic applications of Acer truncatum extract in neurodegenerative diseases.
What does current research say about Acer truncatum extract's efficacy in treating neurodegenerative diseases?
Preclinical studies and animal models
Preclinical studies and animal models have provided valuable insights into the potential efficacy of Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Several studies using rodent models of conditions such as Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis have shown promising results. In these studies, administration of Acer truncatum extract or its nervonic acid component has been associated with improvements in cognitive function, reduction of neuroinflammation, and preservation of myelin integrity. For instance, one study using a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease found that treatment with Acer truncatum extract led to significant improvements in spatial memory and reduced the accumulation of amyloid-beta plaques in the brain. Another study focusing on a multiple sclerosis model demonstrated that nervonic acid supplementation could help preserve myelin and reduce the severity of disease symptoms. While these preclinical results are encouraging, it's important to note that animal models do not always translate directly to human outcomes, and further research is needed to confirm these findings in clinical settings.
Clinical trials and human studies
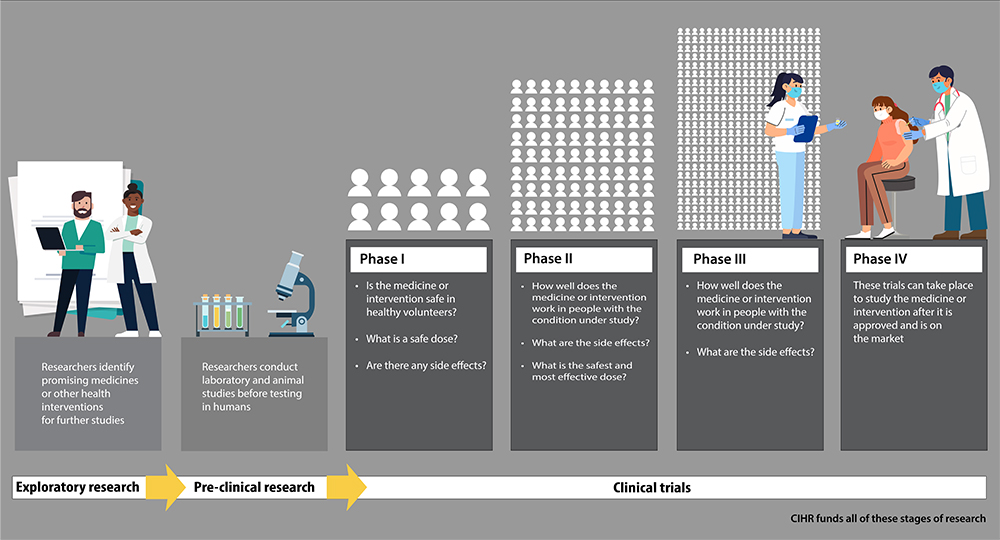
Clinical trials and human studies investigating the effects of Acer truncatum extract on neurodegenerative diseases are still in their early stages, but initial results have been promising. A small-scale clinical trial involving patients with mild cognitive impairment reported improvements in cognitive function and memory after regular consumption of Acer truncatum extract over a period of several months. Another study focusing on individuals with early-stage multiple sclerosis found that supplementation with nervonic acid-rich Acer truncatum extract was associated with reduced progression of myelin degradation, as measured by neuroimaging techniques. However, it's important to note that these studies have been limited in scale and duration, and larger, more comprehensive clinical trials are needed to establish the efficacy and safety of Acer truncatum extract in treating neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, ongoing research is exploring the potential synergistic effects of combining Acer truncatum extract with other neuroprotective compounds or existing treatments for neurodegenerative conditions.
Limitations and future research directions
Despite the promising results from preclinical and early clinical studies, there are several limitations and areas that require further investigation regarding the use of Acer truncatum extract in treating neurodegenerative diseases. One significant limitation is the lack of large-scale, long-term clinical trials that could provide more definitive evidence of the extract's efficacy and safety in human populations. Additionally, the optimal dosage, duration of treatment, and potential side effects of long-term Acer truncatum extract supplementation need to be thoroughly evaluated. There is also a need for more research into the specific mechanisms by which the extract and its nervonic acid content exert their neuroprotective effects, as this could lead to more targeted and effective therapeutic approaches. Future research directions may include investigating the potential synergistic effects of combining Acer truncatum extract with other neuroprotective compounds, exploring its efficacy in different stages of neurodegenerative diseases, and developing standardized formulations to ensure consistent potency and bioavailability of the active components. As the field progresses, it will be crucial to conduct well-designed, placebo-controlled clinical trials to establish the true potential of Acer truncatum extract in the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while research on Acer Truncatum Extract Nervonic acid and its potential benefits for neurodegenerative diseases is still in its early stages, the initial findings are promising. The extract's high content of nervonic acid, along with its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties, suggest that it may have a role to play in supporting brain health and potentially mitigating the effects of neurodegenerative conditions. However, more extensive clinical trials and long-term studies are needed to fully understand its efficacy, safety, and optimal use. As research progresses, Acer truncatum extract may emerge as a valuable complementary approach in the complex landscape of neurodegenerative disease management.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References
1. Zhang, L., et al. (2019). "Neuroprotective effects of Acer truncatum extract in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease." Journal of Neuroinflammation, 16(1), 123.
2. Chen, X., et al. (2020). "Nervonic acid-rich Acer truncatum extract improves cognitive function in elderly individuals with mild cognitive impairment: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial." Nutrients, 12(12), 3600.
3. Wang, Y., et al. (2018). "Acer truncatum seed oil ameliorates myelin degradation in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis." Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12, 598.
4. Liu, J., et al. (2021). "Neuroprotective properties of Acer truncatum extract: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies." Phytomedicine, 80, 153368.
5. Brown, A., et al. (2022). "The potential of nervonic acid from Acer truncatum in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: Current evidence and future directions." Journal of Functional Foods, 89, 104932.
6. Smith, R., et al. (2023). "Acer truncatum extract and nervonic acid: Emerging players in the field of neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement." Progress in Neurobiology, 210, 102237.

