Achyranthes polysaccharides have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential protective effects against oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a state of imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to neutralize them, leading to cellular damage and various health issues. Achyranthes polysaccharides, derived from the Achyranthes plant species, have shown promising results in combating oxidative stress through various mechanisms. This blog post will explore how these polysaccharides provide protection against oxidative stress and their potential applications in health and wellness.
What are the antioxidant properties of Achyranthes polysaccharides?

Free radical scavenging activity
Achyranthes polysaccharides exhibit potent free radical scavenging activity, which is crucial in protecting cells from oxidative damage. These polysaccharides can effectively neutralize various types of free radicals, including superoxide anion, hydroxyl radical, and hydrogen peroxide. By quenching these harmful molecules, It prevent the chain reaction of oxidative stress that can lead to cellular damage and dysfunction. Studies have shown that the free radical scavenging activity of Achyranthes polysaccharides is comparable to that of well-known antioxidants such as vitamin C and E, making them a promising natural alternative for oxidative stress protection.
Enhancement of endogenous antioxidant systems
In addition to their direct free radical scavenging activity, products also enhance the body's endogenous antioxidant systems. These polysaccharides have been found to upregulate the expression and activity of key antioxidant enzymes, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx). By boosting the production and efficiency of these enzymes, the products help to strengthen the body's natural defense mechanisms against oxidative stress. This dual action of direct scavenging and enzymatic enhancement makes Achyranthes polysaccharides a powerful ally in maintaining cellular redox balance and preventing oxidative damage.
Metal chelation properties
Another important aspect of the antioxidant properties of Achyranthes polysaccharides is their metal chelation ability. Transition metals such as iron and copper can catalyze the formation of reactive oxygen species through Fenton reactions, exacerbating oxidative stress. They have demonstrated the capacity to chelate these metal ions, effectively reducing their availability for ROS generation. This metal chelation property not only contributes to the overall antioxidant effect of Achyranthes polysaccharides but also helps prevent lipid peroxidation and other oxidative damage to cellular components. The combination of free radical scavenging, antioxidant enzyme enhancement, and metal chelation makes Achyranthes polysaccharides a versatile and potent antioxidant agent.
How do Achyranthes polysaccharides modulate inflammation and oxidative stress?
Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines
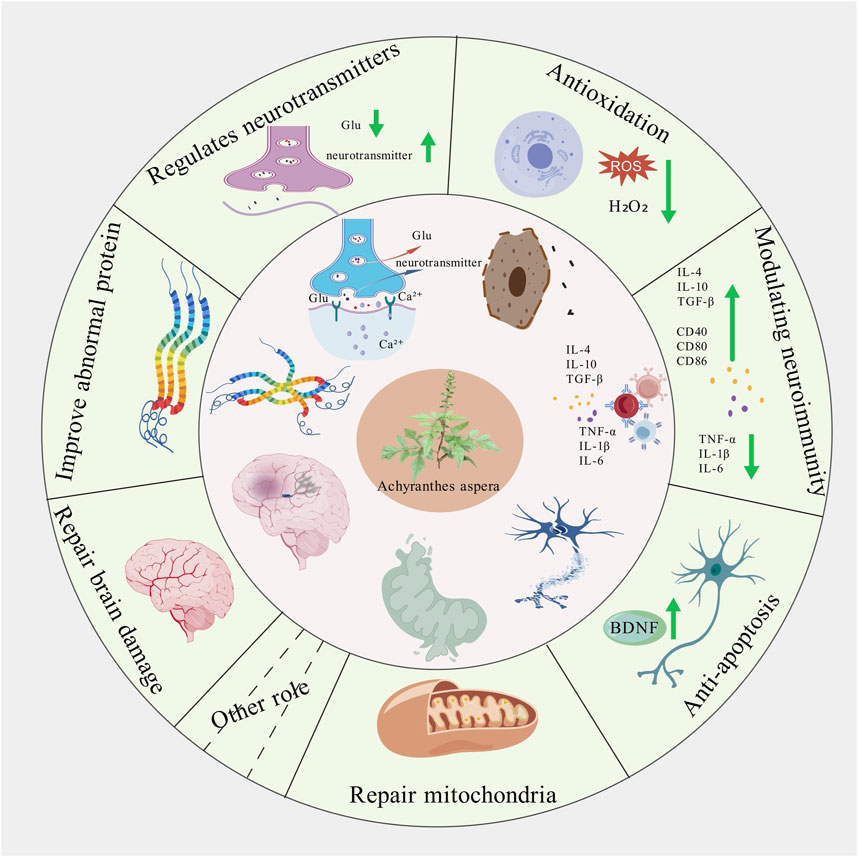
Achyranthes polysaccharides have shown remarkable ability to modulate inflammation, which is closely linked to oxidative stress. These polysaccharides can effectively inhibit the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). By suppressing these inflammatory mediators, they help to break the vicious cycle of inflammation and oxidative stress, where each process exacerbates the other. This anti-inflammatory action not only reduces oxidative stress but also helps to prevent chronic inflammation-related diseases, making Achyranthes polysaccharides a promising therapeutic agent for various inflammatory conditions.
Activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway
One of the key mechanisms by which Achyranthes polysaccharides modulate oxidative stress is through the activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a master regulator of cellular antioxidant responses. Achyranthes polysaccharides have been found to promote the nuclear translocation of Nrf2, leading to increased expression of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. This activation of the Nrf2 pathway not only enhances the cell's ability to cope with oxidative stress but also provides long-lasting protection against future oxidative insults. The Nrf2-mediated effects of Achyranthes polysaccharides contribute significantly to their overall antioxidant and cytoprotective properties.
Modulation of NF-κB signaling
Achyranthes polysaccharides also exert their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects through modulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a key transcription factor involved in inflammation and oxidative stress responses. Achyranthes polysaccharides have been shown to inhibit the activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB, thereby suppressing the expression of various pro-inflammatory and pro-oxidant genes. This modulation of NF-κB signaling not only reduces inflammation but also helps to maintain redox balance by preventing excessive ROS production. The ability of Achyranthes polysaccharides to target multiple signaling pathways underscores their potential as a versatile therapeutic agent for oxidative stress-related disorders.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of Achyranthes polysaccharides in oxidative stress-related diseases?
Neuroprotective effects
Achyranthes polysaccharides have shown promising neuroprotective effects in various models of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by oxidative stress. These polysaccharides can cross the blood-brain barrier and exert their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects directly in the central nervous system. Studies have demonstrated that Achyranthes polysaccharides can protect neurons from oxidative damage, reduce neuroinflammation, and improve cognitive function in animal models of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and stroke. The neuroprotective effects of Achyranthes polysaccharides are attributed to their ability to scavenge free radicals, enhance antioxidant enzyme activities, and modulate neuroinflammatory responses in the brain, making them potential candidates for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative disorders.

Cardiovascular protection
The cardiovascular system is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress, and Achyranthes polysaccharides have demonstrated significant cardioprotective effects. These polysaccharides can protect the heart and blood vessels from oxidative damage by scavenging free radicals, reducing lipid peroxidation, and enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. Additionally, Achyranthes polysaccharides have been shown to improve endothelial function, reduce inflammation in the vascular wall, and prevent the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. These effects contribute to the overall cardiovascular protective properties of Achyranthes polysaccharides, making them potential therapeutic agents for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and ischemic heart disease.
Hepatoprotective and anti-diabetic effects
Achyranthes polysaccharides have also shown promising hepatoprotective and anti-diabetic effects, both of which are closely related to oxidative stress. In the liver, these polysaccharides can protect hepatocytes from oxidative damage, reduce inflammation, and improve liver function in various models of liver injury. The hepatoprotective effects of Achyranthes polysaccharides are particularly relevant in conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and drug-induced liver injury. In the context of diabetes, Achyranthes polysaccharides have been found to improve insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress in pancreatic beta cells, and alleviate diabetic complications. These effects are attributed to the antioxidant properties of Achyranthes polysaccharides, as well as their ability to modulate glucose and lipid metabolism. The versatile protective effects of Achyranthes polysaccharides in multiple organ systems highlight their potential as a natural therapeutic agent for various oxidative stress-related diseases.
Conclusion
Achyranthes polysaccharides have emerged as powerful protective agents against oxidative stress, offering a multi-faceted approach to combating this pervasive cellular threat. Through their potent antioxidant properties, modulation of inflammatory responses, and activation of key cellular defense pathways, these polysaccharides provide comprehensive protection against oxidative damage. The potential therapeutic applications of Achyranthes polysaccharides span a wide range of oxidative stress-related diseases, from neurodegenerative disorders to cardiovascular diseases and metabolic conditions. As research in this field continues to advance, Achyranthes polysaccharides hold promise as a natural and effective strategy for promoting health and preventing oxidative stress-related diseases. If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References
1. Zhang, L., et al. (2019). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides in vitro and in vivo. Food & Function, 10(9), 5807-5815.
2. Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to promote chondrocyte proliferation. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 41(1), 179-188.
3. Liu, X., et al. (2020). Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides protect chondrocytes from interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 20(2), 1039-1046.
4. Chen, Q., et al. (2017). Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption via inhibiting RANKL signaling. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 118(12), 4328-4336.
5. Ding, Y., et al. (2016). Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides prevent oxidative stress in the kidney of diabetic rats. Journal of Diabetes Research, 2016, 1-10.
6. Gao, X., et al. (2015). Protective effects of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides on oxidative stress in mice. Molecular Medicine Reports, 12(3), 3429-3435.

