Honokiol Extract Magnolol is a powerful natural compound derived from the bark of magnolia trees. Known for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties, proper storage is crucial to maintain its efficacy. This blog post will guide you through the best practices for storing Honokiol Extract Magnolol to ensure you get the most out of this valuable supplement.

What is the ideal temperature for storing Honokiol Extract Magnolol?
Temperature plays a critical role in preserving the potency and stability of Honokiol Extract Magnolol. The ideal storage temperature for this compound is generally between 59°F to 77°F (15°C to 25°C). This range is considered room temperature and is suitable for maintaining the extract's chemical structure and therapeutic properties.
However, it's important to note that extreme temperatures can potentially degrade the quality of Honokiol Extract Magnolol. Exposure to high temperatures, especially those above 86°F (30°C), can accelerate the breakdown of the active compounds, reducing their effectiveness. Similarly, freezing temperatures below 32°F (0°C) can also negatively impact the extract's stability.
To ensure optimal storage conditions, consider the following tips:
- Store the extract in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Avoid keeping the product in areas prone to temperature fluctuations, such as near windows or heating vents.
- If you live in a particularly hot climate, consider storing the extract in a refrigerator, but be sure to bring it to room temperature before use.
- When traveling, try to maintain a consistent temperature for the extract by using insulated containers or coolers if necessary.
By maintaining a stable temperature within the recommended range, you can help preserve the potency and extend the shelf life of your Honokiol Extract Magnolol.
How long can Honokiol Extract Magnolol be stored before it expires?
The shelf life of Honokiol Extract Magnolol can vary depending on several factors, including the extraction method, packaging, and storage conditions. Generally, when stored properly, Honokiol Extract Magnolol can maintain its potency for up to two years from the date of manufacture.
However, it's essential to pay attention to the expiration date provided by the manufacturer on the product packaging. This date is typically based on stability testing and represents the period during which the extract is expected to retain its full potency and safety when stored as recommended.
To maximize the shelf life of your Honokiol Extract Magnolol:
- Always check the expiration date before purchasing and using the product.
- Store the extract in its original, airtight container to protect it from moisture and air exposure.
- Keep the container tightly sealed when not in use to prevent oxidation.
- Avoid transferring the extract to different containers, as this can introduce contaminants and compromise its quality.
- If you notice any changes in color, smell, or consistency, it's best to discard the product, even if it hasn't reached its expiration date.
While Honokiol Extract Magnolol may still be safe to use after its expiration date, its potency and effectiveness may be reduced. For optimal results, it's recommended to use the product within the specified shelf life and replace it once it expires.
Can exposure to light affect the quality of Honokiol Extract Magnolol?
Yes, exposure to light, particularly direct sunlight and UV radiation, can significantly affect the quality and potency of Honokiol Extract Magnolol. Light exposure can initiate photochemical reactions that may alter the chemical structure of the active compounds, potentially reducing their therapeutic effects.
The photosensitivity of Honokiol Extract Magnolol is due to its complex molecular structure, which contains various light-reactive functional groups. When exposed to light, these compounds can undergo oxidation, isomerization, or other chemical changes that may diminish their biological activity.
To protect Honokiol Extract Magnolol from light-induced degradation:
- Store the extract in opaque or amber-colored containers that block out light.
- Keep the product in a dark place, such as a closed cabinet or drawer.
- Avoid leaving the extract exposed to sunlight or artificial light for extended periods.
- When using the product, try to minimize its exposure to light by closing the container promptly after each use.
- If the original packaging is not light-resistant, consider transferring the extract to a suitable container that offers better protection.
It's worth noting that some manufacturers may incorporate light-protective additives or use specialized packaging to enhance the photostability of Honokiol Extract Magnolol. However, it's still crucial to take additional precautions to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the product.
Conclusion
By following these storage guidelines for temperature, shelf life, and light exposure, you can help maintain the quality and potency of your Honokiol Extract Magnolol. Proper storage not only extends the product's lifespan but also ensures that you receive the full range of potential health benefits associated with this remarkable natural compound.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
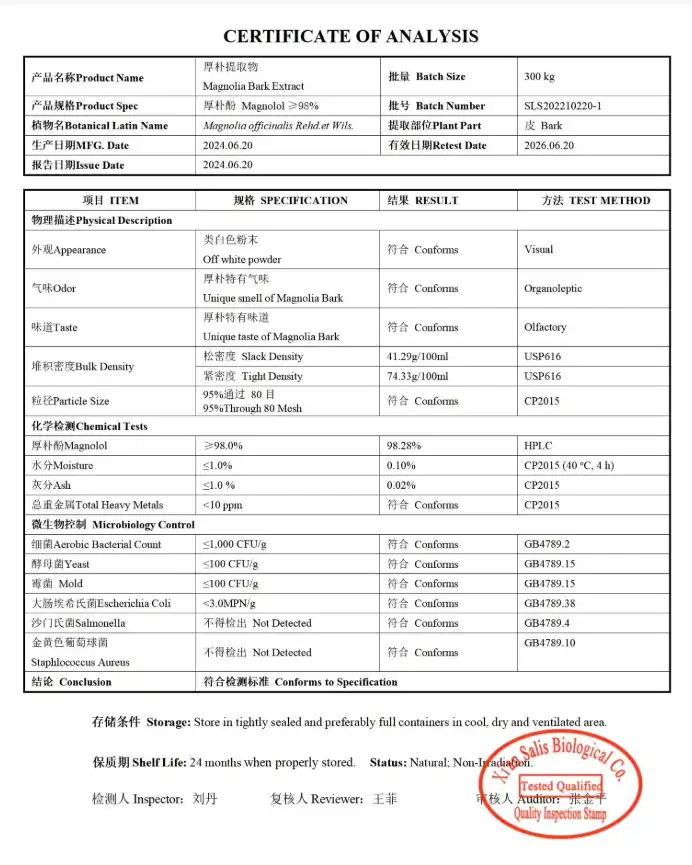
References
1. Lee, Y. J., et al. (2011). Therapeutic applications of compounds in the Magnolia family. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 130(2), 157-176.
2. Woodbury, A., et al. (2013). Neuro-modulating effects of honokiol: a review. Frontiers in Neurology, 4, 130.
3. Fried, L. E., & Arbiser, J. L. (2009). Honokiol, a multifunctional antiangiogenic and antitumor agent. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 11(5), 1139-1148.
4. Shen, J. L., et al. (2010). Honokiol and magnolol as multifunctional antioxidative molecules for dermatologic disorders. Molecules, 15(9), 6452-6465.
5. Chiu, J. H., et al. (2008). Molecular mechanism of the synergistic effects of magnolol and honokiol from Magnolia officinalis on human hepatoma cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 31(1), 62-69.
6. Xu, Q., et al. (2003). Antioxidant effect of magnolol and honokiol from Magnolia officinalis and its application in cosmetics. Journal of Cosmetic Science, 54(5), 451-461.

