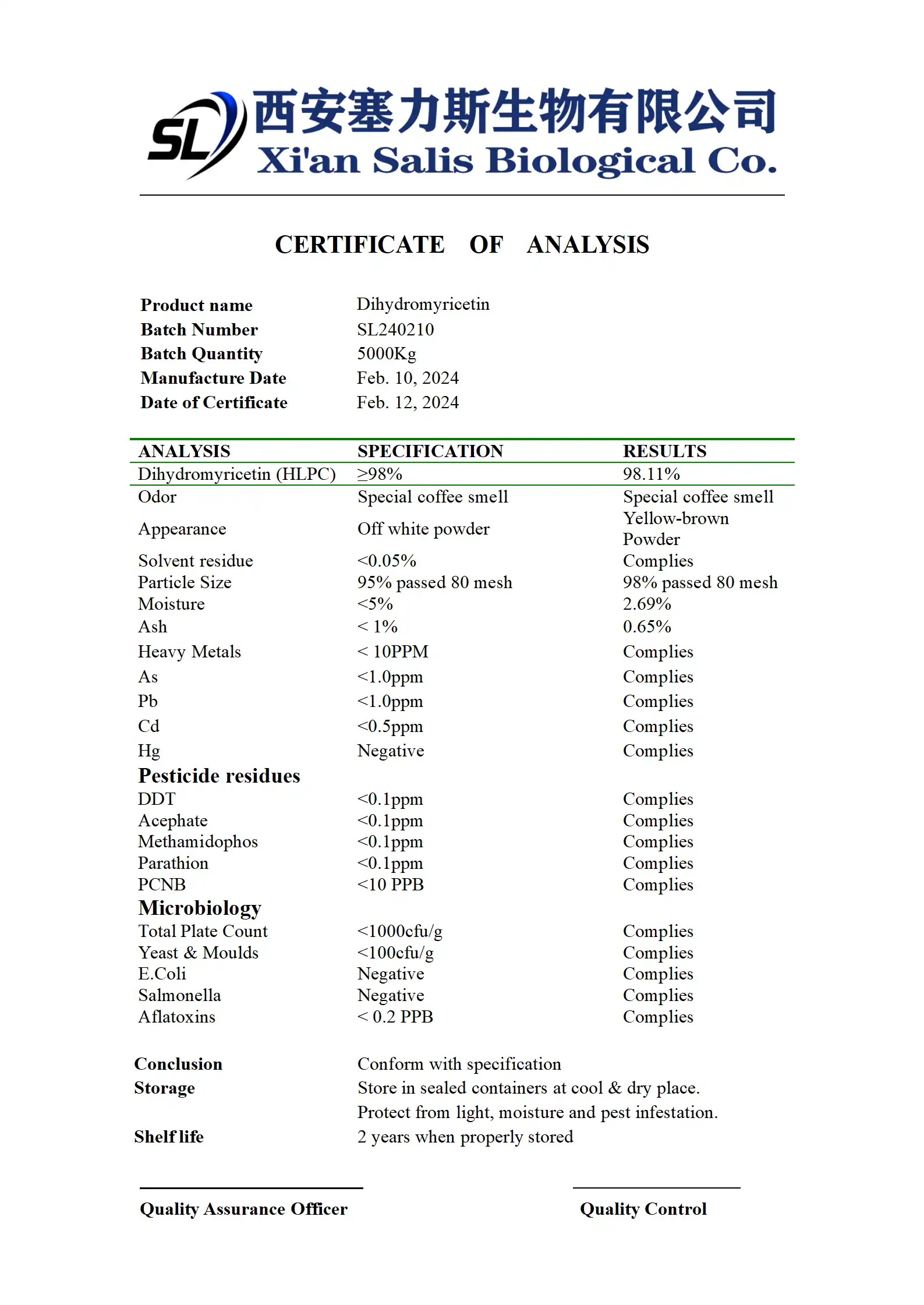
Dihydromyricetin (DHM) powder has gained attention in recent years for its potential liver-protective properties. Derived from the Japanese raisin tree (Hovenia dulcis), this natural compound has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries. As more people become interested in natural remedies for liver health, the question arises: Is Dihydromyricetin Powder effective for liver detoxification? In this blog post, we'll explore the science behind DHM and its potential benefits for liver health.

How does Dihydromyricetin work in the body?
Dihydromyricetin Powder works through various mechanisms in the body, primarily targeting the liver and metabolic processes. When consumed, DHM is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body, with a significant concentration reaching the liver. Once in the liver, DHM exerts its effects through several pathways:
- Antioxidant properties: DHM is a potent antioxidant, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage liver cells. This antioxidant activity is crucial for protecting the liver from oxidative stress, which is often associated with alcohol consumption and other toxins.
- Enzyme activation: DHM has been shown to activate certain enzymes in the liver, particularly alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). These enzymes are responsible for breaking down alcohol and its toxic byproducts, such as acetaldehyde. By enhancing the activity of these enzymes, DHM may help accelerate the metabolism of alcohol and reduce its harmful effects on the liver.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Chronic inflammation is a significant factor in liver damage and disease. DHM has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce liver inflammation and promote healing.
- Lipid metabolism regulation: Research suggests that DHM may help regulate lipid metabolism in the liver. This could potentially prevent the accumulation of fat in liver cells, a condition known as fatty liver disease.
- GABA receptor modulation: DHM has been found to interact with GABA receptors in the brain, which may contribute to its anti-anxiety and sleep-promoting effects. While not directly related to liver function, this action may indirectly support liver health by reducing stress and improving sleep quality.
The combination of these effects makes DHM a promising compound for supporting liver health and potentially aiding in detoxification processes. However, it's important to note that while these mechanisms have been observed in laboratory and animal studies, more human clinical trials are needed to fully understand the extent of DHM's effects in the human body.
What are the benefits of taking Dihydromyricetin for liver health?
Dihydromyricetin Powder has shown several potential benefits for liver health, based on both traditional use and modern scientific research. While more studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy in humans, the existing evidence suggests that DHM may offer the following benefits for liver health:
- Liver protection: One of the most significant potential benefits of DHM is its ability to protect liver cells from damage. Studies have shown that DHM can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver, which are major contributors to liver damage and disease. This protective effect may be particularly beneficial for individuals who consume alcohol regularly or are exposed to other liver-damaging toxins.
- Enhanced alcohol metabolism: DHM has been found to increase the activity of enzymes responsible for breaking down alcohol in the liver. This can potentially lead to faster alcohol metabolism and reduced hangover symptoms. By accelerating the breakdown of alcohol and its toxic byproducts, DHM may help minimize the negative effects of alcohol on the liver.
- Fatty liver prevention: Some research suggests that DHM may help prevent the accumulation of fat in liver cells, a condition known as fatty liver disease. This is particularly important as fatty liver disease is becoming increasingly common and can lead to more serious liver conditions if left untreated.
- Antioxidant support: As a potent antioxidant, DHM helps neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, including those that can damage liver cells. This antioxidant activity may contribute to overall liver health and function.
- Improved liver enzyme levels: Some studies have shown that DHM supplementation may help normalize liver enzyme levels, which are often elevated in individuals with liver damage or disease. This normalization of liver enzymes could indicate improved liver function and health.
- Potential anti-fibrotic effects: Preliminary research suggests that DHM may have anti-fibrotic properties, potentially helping to prevent or reduce liver fibrosis, a condition characterized by the accumulation of scar tissue in the liver.
- Support for overall detoxification: While the liver is the body's primary detoxification organ, DHM's protective and supportive effects on liver function may indirectly enhance the body's overall detoxification processes.
It's important to note that while these potential benefits are promising, more research, particularly in human clinical trials, is needed to fully establish the effectiveness of DHM for liver health. Additionally, DHM should not be considered a substitute for a healthy lifestyle or medical treatment for liver conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have existing liver issues or are taking medications.
Can Dihydromyricetin help with alcohol-induced liver damage?
Dihydromyricetin Powder has shown promising potential in addressing alcohol-induced liver damage, making it a subject of interest for both researchers and individuals seeking natural remedies for alcohol-related liver issues. While more human studies are needed to fully confirm its efficacy, existing research provides encouraging insights into how DHM might help mitigate the harmful effects of alcohol on the liver:
- Accelerated alcohol metabolism: One of the primary ways DHM may help with alcohol-induced liver damage is by enhancing the activity of alcohol-metabolizing enzymes. Studies have shown that DHM can increase the activity of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), the two main enzymes responsible for breaking down alcohol in the liver. By accelerating alcohol metabolism, DHM may reduce the time alcohol spends in the body, potentially minimizing its harmful effects on the liver.
- Reduction of oxidative stress: Alcohol consumption generates a significant amount of oxidative stress in the liver, which can lead to cell damage and inflammation. DHM's potent antioxidant properties may help neutralize these harmful free radicals, protecting liver cells from oxidative damage. This antioxidant effect could be particularly beneficial in preventing long-term liver damage associated with chronic alcohol consumption.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Chronic alcohol use often leads to liver inflammation, which can progress to more serious conditions like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis. DHM has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in several studies, which could help reduce alcohol-induced liver inflammation and promote healing.
- Prevention of fatty liver: Alcohol consumption is a common cause of fatty liver disease, where excess fat accumulates in liver cells. Some research suggests that DHM may help prevent this fat accumulation, potentially by regulating lipid metabolism in the liver. This could be particularly beneficial for individuals at risk of developing alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Hangover reduction: While not directly related to liver damage, DHM's ability to reduce hangover symptoms may indirectly benefit liver health by potentially discouraging excessive alcohol consumption. Studies have shown that DHM can alleviate several hangover symptoms, which may be due to its effects on alcohol metabolism and GABA receptors in the brain.
- Liver enzyme normalization: Elevated liver enzymes are often an indicator of liver damage or stress. Some studies have found that DHM supplementation can help normalize liver enzyme levels in individuals who consume alcohol, suggesting a potential protective effect on liver cells.
- Potential regenerative effects: While more research is needed in this area, some preliminary studies suggest that DHM may have regenerative effects on liver cells. This could potentially aid in the recovery of liver tissue that has been damaged by alcohol consumption.
It's important to emphasize that while these potential benefits are promising, DHM should not be viewed as a license to drink excessively or as a cure for alcohol-related liver diseases. The most effective way to prevent alcohol-induced liver damage is to moderate or abstain from alcohol consumption. However, for individuals who do consume alcohol, DHM may offer some protective benefits when used as part of a comprehensive approach to liver health.
Furthermore, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using DHM or any supplement, especially if you have existing liver conditions or are taking medications. While DHM appears to have a good safety profile, more long-term studies in humans are needed to fully understand its effects and potential interactions.
Conclusion
While Dihydromyricetin powder shows promise in supporting liver health and potentially mitigating some effects of alcohol-induced liver damage, it should be viewed as a complementary approach rather than a standalone solution. A healthy lifestyle, including moderate alcohol consumption (if any), a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hydration, remains the cornerstone of liver health and overall well-being.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
References
1. Shen, Y., Lindemeyer, A. K., Gonzalez, C., Shao, X. M., Spigelman, I., Olsen, R. W., & Liang, J. (2012). Dihydromyricetin as a novel anti-alcohol intoxication medication. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(1), 390-401.
2. Hou, X. L., Tong, Q., Wang, W. Q., Shi, C. Y., Xiong, W., Chen, J., ... & Fang, J. G. (2015). Suppression of inflammatory responses by dihydromyricetin, a flavonoid from Ampelopsis grossedentata, via inhibiting the activation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Journal of Natural Products, 78(7), 1689-1696.
3. Chen, S., Zhao, X., Wan, J., Ran, L., Qin, Y., Wang, X., ... & Shi, C. (2015). Dihydromyricetin improves glucose and lipid metabolism and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Pharmacological Research, 99, 74-81.
4. Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, T., Li, B., Li, H., Wang, Z., & Yang, B. (2018). Resveratrol, a natural polyphenol, attenuates EtOH-induced reactive oxygen species production in hepatocytes. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 24(15), 1644-1654.
5. Liang, J., & Olsen, R. W. (2014). Alcohol use disorders and current pharmacological therapies: the role of GABA(A) receptors. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 35(8), 981-993.
6. Wu, S., Liu, Y., Guo, W., Hou, B., Zhang, X., Zhao, X., ... & Wang, Q. (2019). Protective effects of dihydromyricetin against γ-radiation-induced DNA damage and cell apoptosis in mouse spleen lymphocytes. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 123, 172-180.

