Genistein powder, derived from soybeans, has gained popularity as a dietary supplement due to its potential health benefits. As more people incorporate it into their daily routines, questions about its safety and efficacy have arisen. This article explores the safety of daily genistein powder consumption and addresses some common concerns.
What are the potential benefits of taking Genistein Powder?
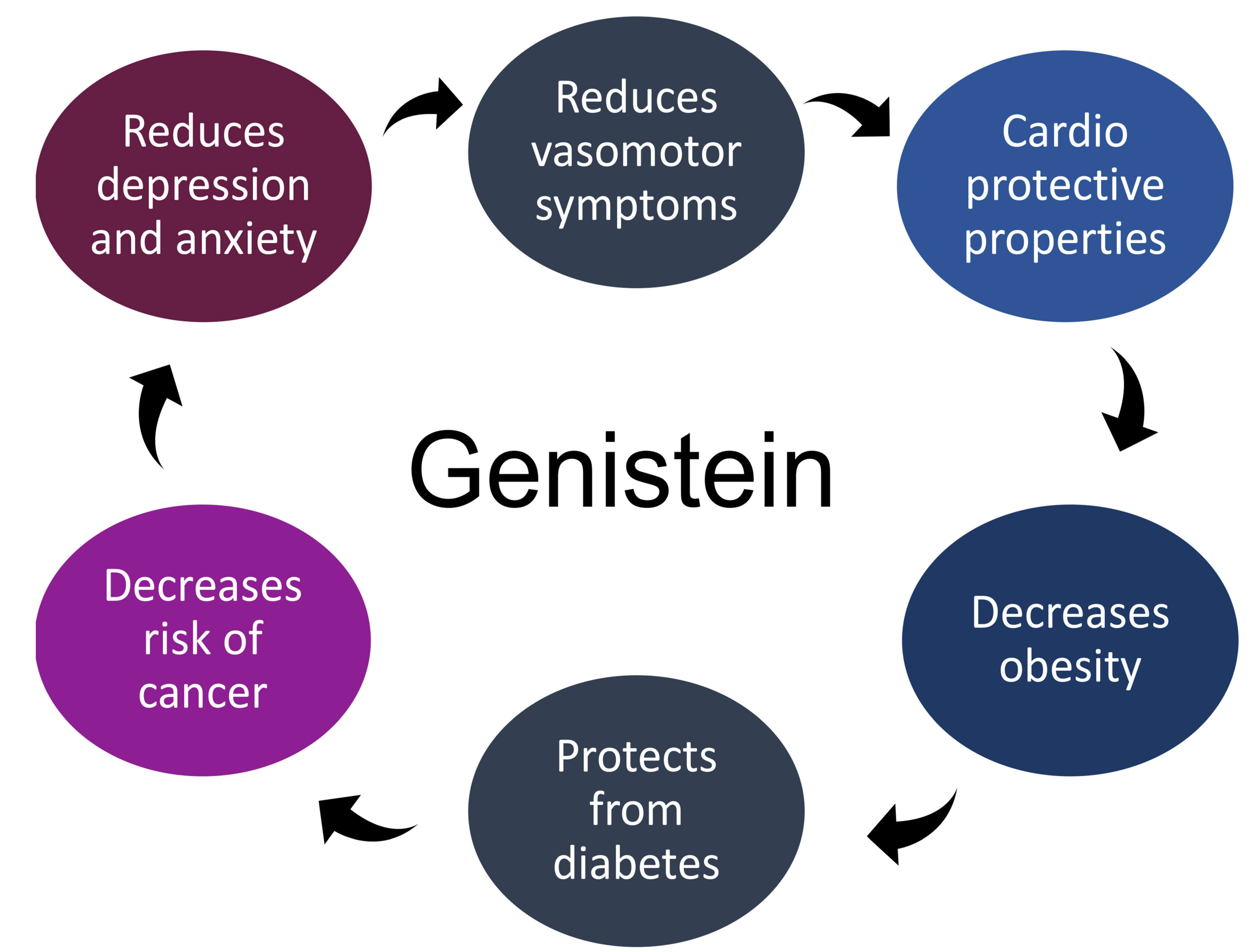
Genistein powder has been associated with numerous potential health benefits, making it an attractive supplement for many individuals. Research suggests that genistein may offer several advantages:
- Antioxidant properties: Genistein is a potent antioxidant that can help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. This property may contribute to overall health and potentially reduce the risk of certain chronic diseases.
- Bone health support: Some studies indicate that genistein may help maintain bone density, particularly in postmenopausal women. It may influence bone metabolism and potentially reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
- Cardiovascular health: Genistein has been associated with improved cardiovascular health by potentially lowering cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Menopausal symptom relief: As a phytoestrogen, genistein may help alleviate some menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats, by mimicking the effects of estrogen in the body.
- Potential anti-cancer properties: While more research is needed, some studies suggest that genistein may have anti-cancer properties, particularly in breast and prostate cancers. However, it's important to note that these findings are preliminary and should not be considered as a replacement for conventional cancer treatments.
- Skin health: Genistein's antioxidant properties may contribute to improved skin health by protecting against UV damage and potentially reducing the signs of aging.
- Cognitive function: Some research indicates that genistein may have neuroprotective effects, potentially benefiting cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
While these potential benefits are promising, it's crucial to remember that individual results may vary, and more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of daily genistein powder consumption. As with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating genistein powder into your daily routine.
How much Genistein Powder should I take daily?
Determining the appropriate dosage of genistein powder is crucial for maximizing its potential benefits while minimizing any potential risks. However, it's important to note that there is no universally agreed-upon standard dosage for genistein powder. The optimal amount can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, health status, and the specific health goals of the individual.
Here are some general guidelines and considerations for genistein powder dosage:
- Research-based dosages: Many studies investigating the effects of genistein have used dosages ranging from 30 to 120 mg per day. Some research has suggested that doses as low as 20 mg per day may provide certain health benefits.
- Dietary intake: It's worth considering that individuals who consume a diet rich in soy products may already have a significant intake of genistein. The average dietary intake of genistein in Asian countries, where soy consumption is high, is estimated to be around 20-80 mg per day.
- Supplement formulations: Commercial genistein powder supplements often come in various strengths, typically ranging from 25 to 100 mg per serving. Always follow the manufacturer's recommended dosage unless otherwise advised by a healthcare professional.
- Individual factors: The appropriate dosage may depend on the specific health condition being addressed. For example, studies on bone health have used doses ranging from 54 to 120 mg daily, while research on menopausal symptoms has often used doses around 50-60 mg per day.
- Bioavailability considerations: The body's ability to absorb and utilize genistein can vary. Some studies suggest that taking genistein with food, particularly fat, may enhance its absorption.
- Duration of use: Most studies on genistein supplementation have been conducted over periods ranging from a few weeks to several months. Long-term effects of daily genistein powder consumption beyond these durations are not yet well-established.
It's crucial to emphasize that while these guidelines provide a general framework, the ideal dosage of genistein powder can vary significantly from person to person. Factors such as overall health, existing medical conditions, medications, and individual response to the supplement all play a role in determining the appropriate amount.
Before starting any new supplement regimen, including genistein powder, it's highly recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific health profile and goals. Additionally, they can help monitor your response to the supplement and adjust the dosage if necessary.
Remember that more is not always better when it comes to supplements. Taking excessively high doses of genistein powder may not provide additional benefits and could potentially lead to adverse effects. Start with a lower dose and gradually increase if needed, always under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Lastly, it's important to source genistein powder from reputable manufacturers to ensure product quality and purity. Look for supplements that have been third-party tested and certified to contain the stated amount of genistein.
Are there any interactions between Genistein Powder and medications?
Understanding potential interactions between genistein powder and medications is crucial for ensuring safe consumption, especially for individuals taking multiple supplements or prescription drugs. While genistein is generally considered safe for most people, it can interact with certain medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or causing unwanted side effects.
Here are some important interactions to be aware of:
- Estrogen-based medications: Genistein is a phytoestrogen, meaning it can mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. This property may interfere with estrogen-based medications, including hormone replacement therapy and some birth control pills. The interaction could potentially enhance or diminish the effects of these medications.
- Blood thinners: Some studies suggest that genistein may have mild anticoagulant properties. Therefore, individuals taking blood-thinning medications such as warfarin should exercise caution and consult their healthcare provider before using genistein powder. The combination could potentially increase the risk of bleeding.
- Tamoxifen: This medication, used in breast cancer treatment, works by blocking estrogen receptors. Since genistein can interact with estrogen receptors, it may potentially interfere with tamoxifen's effectiveness. Patients undergoing tamoxifen treatment should discuss genistein supplementation with their oncologist.
- Thyroid medications: Some research indicates that genistein may interfere with the absorption of thyroid hormones. Individuals taking thyroid medications should be cautious and may need to adjust their medication timing or dosage under medical supervision.
- Antibiotics: Genistein may affect the absorption and effectiveness of certain antibiotics. It's advisable to separate the intake of genistein powder and antibiotics by several hours.
- Antidiabetic medications: Genistein has been shown to have potential blood sugar-lowering effects. While this can be beneficial, it may also interact with diabetes medications, potentially leading to hypoglycemia. Close monitoring of blood sugar levels is recommended for diabetic patients using genistein powder.
- Calcium channel blockers: These medications, often used to treat high blood pressure, may interact with genistein. The combination could potentially enhance the blood pressure-lowering effects, necessitating dose adjustments.
- CYP450 enzyme substrates: Genistein may affect the activity of certain enzymes in the liver responsible for metabolizing various medications. This could potentially alter the effectiveness or side effect profile of drugs metabolized by these enzymes.
It's important to note that the severity and likelihood of these interactions can vary based on factors such as the dosage of genistein powder, individual physiology, and the specific medications involved. Furthermore, not all potential interactions have been thoroughly studied, and new findings may emerge as research in this area continues.
To ensure safe consumption of genistein powder alongside medications:
- Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting genistein supplementation, especially if you are taking any medications.
- Provide your healthcare provider with a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal products you are using.
- If you experience any unusual symptoms or changes in your health after starting genistein powder, report them to your healthcare provider promptly.
- Consider working with a healthcare provider who is knowledgeable about both conventional medications and dietary supplements to help manage potential interactions.
- Be cautious about self-prescribing or adjusting medication dosages without professional guidance.
Remember that while genistein powder may offer potential health benefits, it should not be used as a substitute for prescribed medications without medical supervision. The goal is to integrate genistein powder into your health regimen safely and effectively, maximizing its potential benefits while minimizing risks.
Conlusion
Lastly, it's worth noting that the quality and purity of genistein powder can vary between manufacturers. Always choose products from reputable sources and look for third-party testing certifications to ensure you're getting a high-quality supplement. This can help reduce the risk of contaminants or inconsistent dosing that could potentially interact with medications.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
References
1. Křížová, L., Dadáková, K., Kašparovská, J., & Kašparovský, T. (2019). Isoflavones. Molecules, 24(6), 1076.
2. Vitale, D. C., Piazza, C., Melilli, B., Drago, F., & Salomone, S. (2013). Isoflavones: estrogenic activity, biological effect and bioavailability. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 38(1), 15-25.
3. Tham, D. M., Gardner, C. D., & Haskell, W. L. (1998). Potential health benefits of dietary phytoestrogens: a review of the clinical, epidemiological, and mechanistic evidence. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 83(7), 2223-2235.
4. Setchell, K. D. (1998). Phytoestrogens: the biochemistry, physiology, and implications for human health of soy isoflavones. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 68(6), 1333S-1346S.
5. Messina, M. (2010). A brief historical overview of the past two decades of soy and isoflavone research. The Journal of Nutrition, 140(7), 1350S-1354S.
6. Ganai, A. A., & Farooqi, H. (2015). Bioactivity of genistein: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 76, 30-38.
7. Spagnuolo, C., Russo, G. L., Orhan, I. E., Habtemariam, S., Daglia, M., Sureda, A., ... & Nabavi, S. M. (2015). Genistein and cancer: current status, challenges, and future directions. Advances in Nutrition, 6(4), 408-419.
8. Cederroth, C. R., Zimmermann, C., & Nef, S. (2012). Soy, phytoestrogens and their impact on reproductive health. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 355(2), 192-200.
9. Soni, M., Rahardjo, T. B. W., Soekardi, R., Sulistyowati, Y., Lestariningsih, ... & Hogervorst, E. (2014). Phytoestrogens and cognitive function: a review. Maturitas, 77(3), 209-220.
10. Patisaul, H. B., & Jefferson, W. (2010). The pros and cons of phytoestrogens. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 31(4), 400-419.

