Genistein powder, a naturally occurring isoflavone found primarily in soybeans and other legumes, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. As more people turn to natural supplements and nutraceuticals, questions about the safety and efficacy of it have become increasingly common. This blog post aims to explore the safety aspects of it, its potential benefits, and considerations for use, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this popular supplement.

What are the potential health benefits of genistein powder?
Antioxidant properties of genistein powder
Genistein powder is renowned for its potent antioxidant properties, which play a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. This isoflavone has been shown to neutralize harmful molecules that can contribute to various chronic diseases and accelerate the aging process. Research suggests that the antioxidant effects of it may help reduce inflammation throughout the body, potentially lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases, certain types of cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Moreover, the antioxidant capabilities of it have been linked to improved skin health, as it may help protect against UV-induced damage and promote collagen production, leading to a more youthful appearance.
Genistein powder and bone health
One of the most well-studied benefits of it is its positive impact on bone health. This isoflavone has been shown to mimic the effects of estrogen in the body, which is particularly beneficial for postmenopausal women who are at a higher risk of osteoporosis due to declining estrogen levels. Numerous studies have demonstrated that it can help increase bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fractures. It achieves this by promoting osteoblast activity (cells responsible for bone formation) while inhibiting osteoclast activity (cells that break down bone tissue). Additionally, it may enhance calcium absorption in the intestines, further supporting overall bone health. These properties make it a promising natural alternative or complementary approach to conventional osteoporosis treatments.
Potential cancer-fighting properties of genistein powder
It has garnered significant attention in the field of cancer research due to its potential anti-cancer properties. Several studies have suggested that this isoflavone may help inhibit the growth and spread of various types of cancer cells, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer. The mechanisms by which genistein powder exerts its anti-cancer effects are multifaceted. It has been shown to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, inhibit angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors), and modulate various signaling pathways involved in cancer progression. Furthermore, it may enhance the effectiveness of certain chemotherapy drugs, potentially improving treatment outcomes. While more research is needed to fully understand its role in cancer prevention and treatment, the existing evidence suggests that it holds promise as a natural compound with anti-cancer potential.
Are there any side effects associated with genistein powder consumption?
Common side effects of genistein powder
While genistein powder is generally considered safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts, some individuals may experience side effects. The most commonly reported side effects include gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating, gas, and nausea. These symptoms are typically mild and often subside as the body adjusts to the supplement. Some users have also reported headaches, dizziness, and changes in menstrual cycles. It's important to note that these side effects are usually associated with high doses of it or sudden increases in consumption. To minimize the risk of experiencing these side effects, it's recommended to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it over time. Additionally, taking it with food may help reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal issues.
Potential interactions with medications
Genistein powder, like many dietary supplements, has the potential to interact with certain medications. One of the primary concerns is its interaction with estrogen-based medications, such as hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills. Due to its estrogen-like effects, it may either enhance or interfere with the action of these medications, potentially altering their effectiveness. Additionally, it may interact with blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding. Some studies have also suggested that it may interfere with the absorption of certain antibiotics and thyroid medications. Given these potential interactions, it's crucial for individuals taking any medications to consult with their healthcare provider before incorporating it into their supplement regimen. This consultation can help identify any potential risks and ensure that the use of it is safe and appropriate for their specific health situation.
Long-term safety considerations of genistein powder use
While short-term use of genistein powder is generally considered safe for most people, the long-term safety of this supplement is still being studied. Some researchers have raised concerns about the potential effects of prolonged, high-dose genistein powder consumption, particularly in individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions. For example, there is ongoing debate about whether long-term use of high doses of it could potentially stimulate the growth of estrogen-sensitive breast cancer cells in some women. However, it's important to note that current evidence is mixed, and more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects. Another consideration is the impact of it on thyroid function, as some studies have suggested that high doses may interfere with thyroid hormone production in certain individuals. To ensure safe long-term use, it's recommended to use it under the guidance of a healthcare professional, who can monitor for any potential adverse effects and adjust dosage as needed.
How does genistein powder compare to other isoflavone supplements?
Genistein powder vs. daidzein
Genistein powder and daidzein are both isoflavones commonly found in soy products, but they have distinct characteristics and potential health effects. Genistein powder is often considered the more potent of the two, with stronger estrogenic effects and a higher binding affinity for estrogen receptors. This makes genistein powder potentially more effective for addressing menopausal symptoms and supporting bone health. On the other hand, daidzein is known for its ability to be converted into equol by gut bacteria in some individuals, which may provide additional health benefits. When comparing their antioxidant properties, genistein powder generally exhibits stronger antioxidant activity than daidzein. However, both compounds have shown promising results in various studies related to cardiovascular health, cancer prevention, and inflammation reduction. The choice between it and daidzein may depend on individual health goals and how one's body responds to each isoflavone.
Genistein powder vs. soy protein isolate
While both it and soy protein isolate are derived from soybeans, they differ significantly in their composition and potential health benefits. Genistein powder is a concentrated form of a specific isoflavone, whereas soy protein isolate is a protein extract that contains a mixture of isoflavones, including genistein, daidzein, and glycitein. Soy protein isolate is primarily used as a protein source and for its potential cardiovascular benefits, such as lowering cholesterol levels. In contrast, genistein powder is typically used for its more targeted effects on bone health, menopausal symptoms, and potential anti-cancer properties. The concentration of genistein in soy protein isolate is generally much lower than in pure genistein powder supplements, which means that larger quantities of soy protein isolate would need to be consumed to achieve similar levels of genistein intake. Additionally, genistein powder allows for more precise dosing and may be preferable for individuals seeking specific isoflavone-related benefits without the added protein and calories found in soy protein isolate.
Bioavailability and absorption of genistein powder
The bioavailability and absorption of genistein powder are crucial factors in determining its effectiveness as a supplement. Genistein powder is generally well-absorbed by the body, but several factors can influence its bioavailability. The form in which genistein is consumed plays a significant role; aglycone forms (found in fermented soy products and some supplements) are more readily absorbed than glycoside forms (found in most unfermented soy foods). Additionally, the presence of other nutrients can affect genistein absorption. For example, consuming genistein powder with fat may enhance its absorption, while high-fiber diets might decrease it. The gut microbiome also plays a crucial role in genistein metabolism, as certain gut bacteria can convert genistein into more active metabolites. Factors such as age, gender, and individual genetic variations can also influence how efficiently the body absorbs and utilizes genistein powder. To maximize absorption and effectiveness, it's often recommended to take genistein powder supplements with food and to maintain a diverse, healthy gut microbiome.
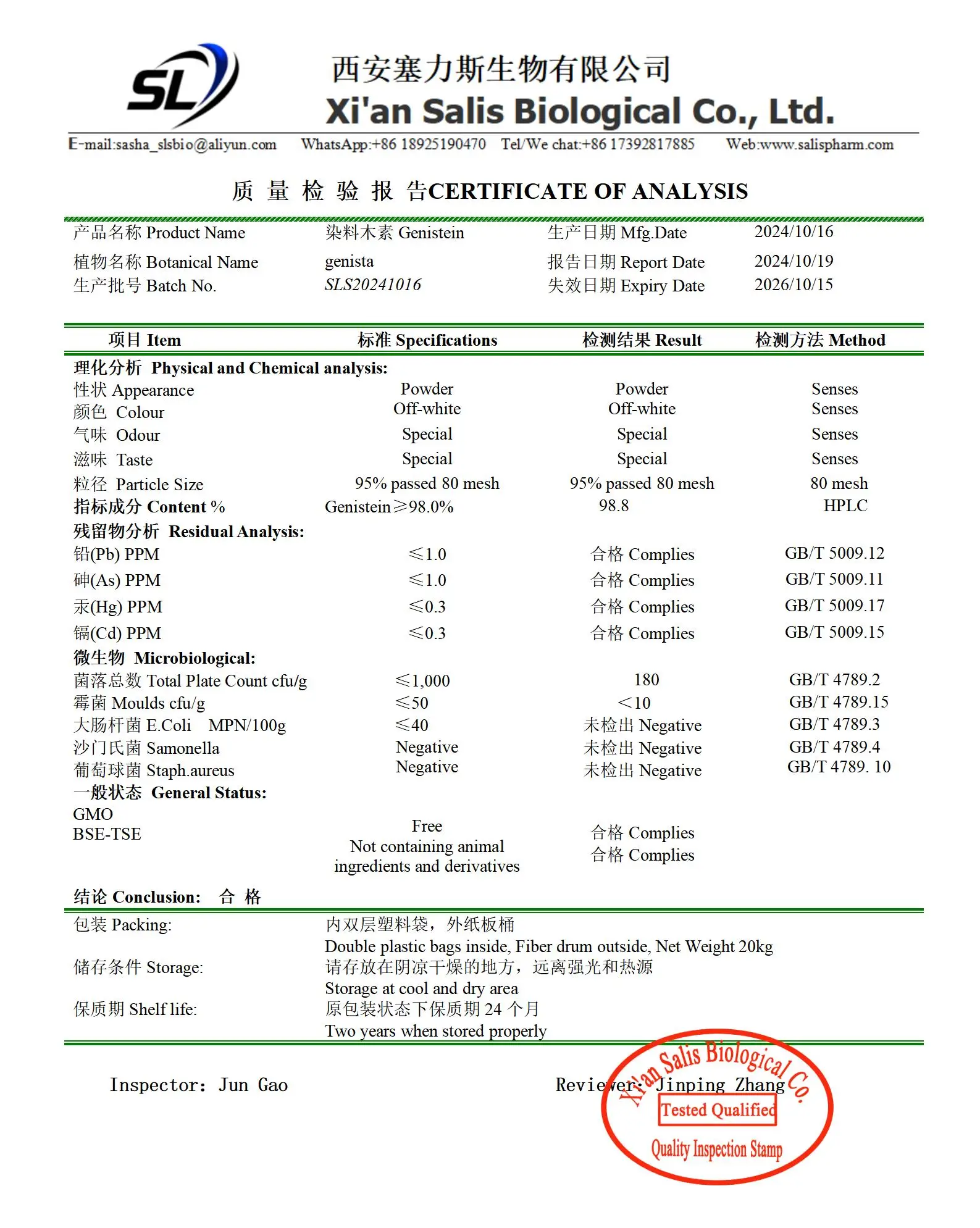
Conclusion
In conclusion, genistein powder is generally considered safe for most people when used appropriately and under professional guidance. Its potential health benefits, including antioxidant properties, bone health support, and possible anti-cancer effects, make it an attractive supplement for many. However, like any supplement, it's not without potential side effects and interactions. It's crucial to consider individual health status, medication use, and long-term safety when deciding to use genistein powder. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure it's safe and appropriate for your specific needs. If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
References
1. Spagnuolo, C., Russo, G. L., Orhan, I. E., Habtemariam, S., Daglia, M., Sureda, A., ... & Nabavi, S. M. (2015). Genistein and cancer: current status, challenges, and future directions. Advances in nutrition, 6(4), 408-419.
2. Setchell, K. D., & Clerici, C. (2010). Equol: history, chemistry, and formation. The Journal of nutrition, 140(7), 1355S-1362S.
3. Ganai, A. A., & Farooqi, H. (2015). Bioactivity of genistein: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 76, 30-38.
4. Taku, K., Melby, M. K., Nishi, N., Omori, T., & Kurzer, M. S. (2011). Soy isoflavones for osteoporosis: an evidence-based approach. Maturitas, 70(4), 333-338.
5. Pavese, J. M., Farmer, R. L., & Bergan, R. C. (2010). Inhibition of cancer cell invasion and metastasis by genistein. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 29(3), 465-482.
6. Sirotkin, A. V., & Harrath, A. H. (2014). Phytoestrogens and their effects. European journal of pharmacology, 741, 230-236.

