Quercetin powder has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential health benefits, particularly in relation to cardiovascular health. As a natural flavonoid found in various fruits and vegetables, quercetin has been the subject of numerous studies investigating its effects on blood pressure. This article will explore the effectiveness of quercetin powder in reducing blood pressure and address some of the most common questions surrounding its use.
How does Quercetin Powder work to lower blood pressure?
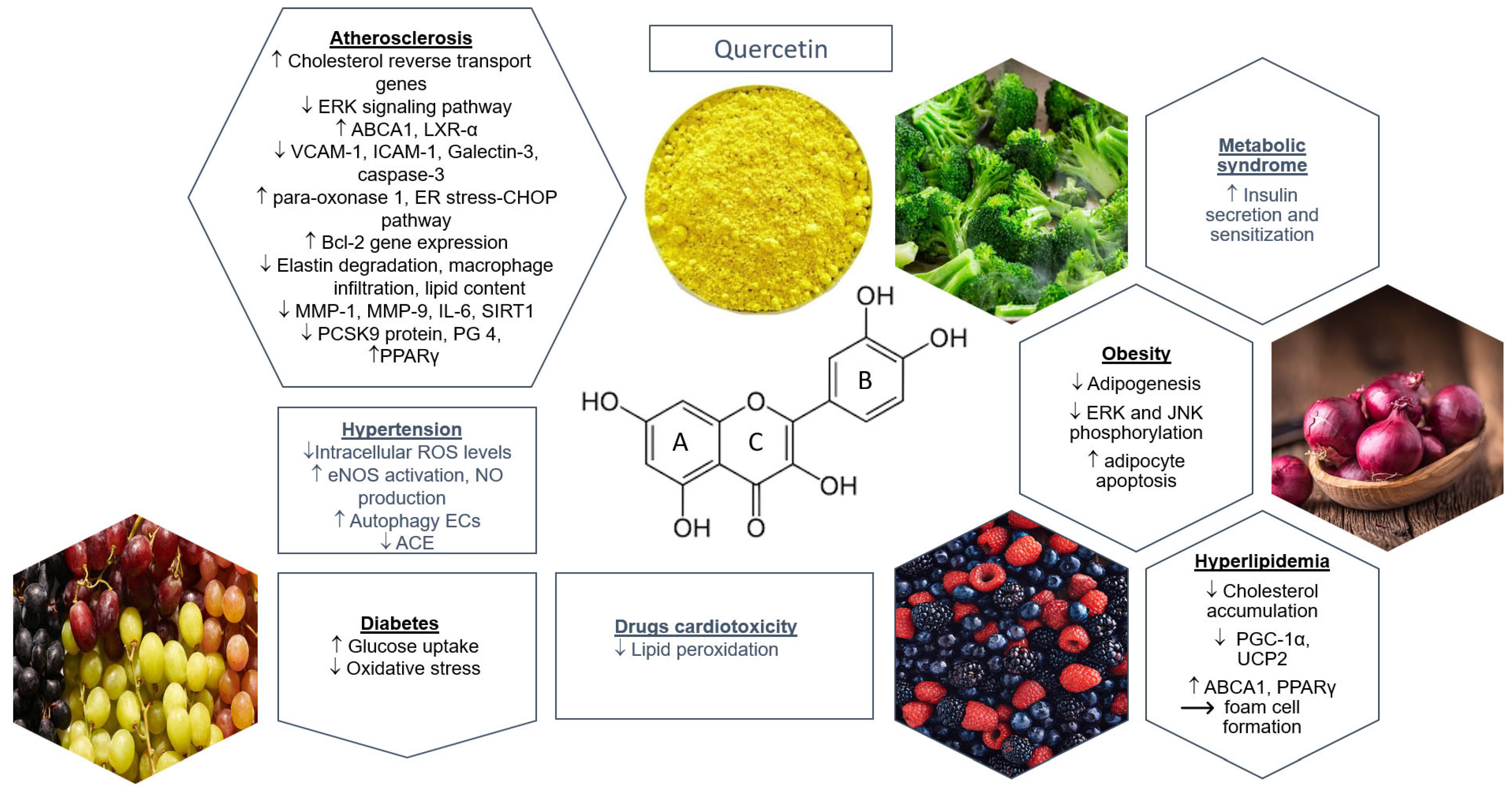
Quercetin powder is believed to lower blood pressure through several mechanisms. Primarily, it acts as a potent antioxidant, helping to reduce oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress is a key factor in the development of hypertension, as it can lead to damage of the blood vessels and impair their ability to dilate properly.
One of the main ways quercetin works to lower blood pressure is by promoting the production of nitric oxide (NO) in the body. Nitric oxide is a crucial molecule that helps relax and dilate blood vessels, allowing for improved blood flow and reduced pressure on arterial walls. By enhancing NO production, quercetin can contribute to better overall cardiovascular function.
Additionally, quercetin has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is often associated with hypertension, and by reducing inflammation in the body, quercetin may help alleviate some of the underlying causes of high blood pressure.
Research has also suggested that quercetin may help regulate the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which plays a crucial role in blood pressure regulation. By modulating this system, quercetin could potentially help maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Furthermore, quercetin has been found to have a mild diuretic effect. This means it can help the body eliminate excess sodium and water, which can contribute to lowering blood pressure. While this effect is not as strong as pharmaceutical diuretics, it may still provide some benefit in managing hypertension.
It's important to note that while these mechanisms have been observed in various studies, the exact extent of quercetin's impact on blood pressure can vary from person to person. Factors such as individual physiology, diet, lifestyle, and overall health status can all influence how effectively quercetin works to lower blood pressure.
What is the recommended dosage of Quercetin Powder for blood pressure control?
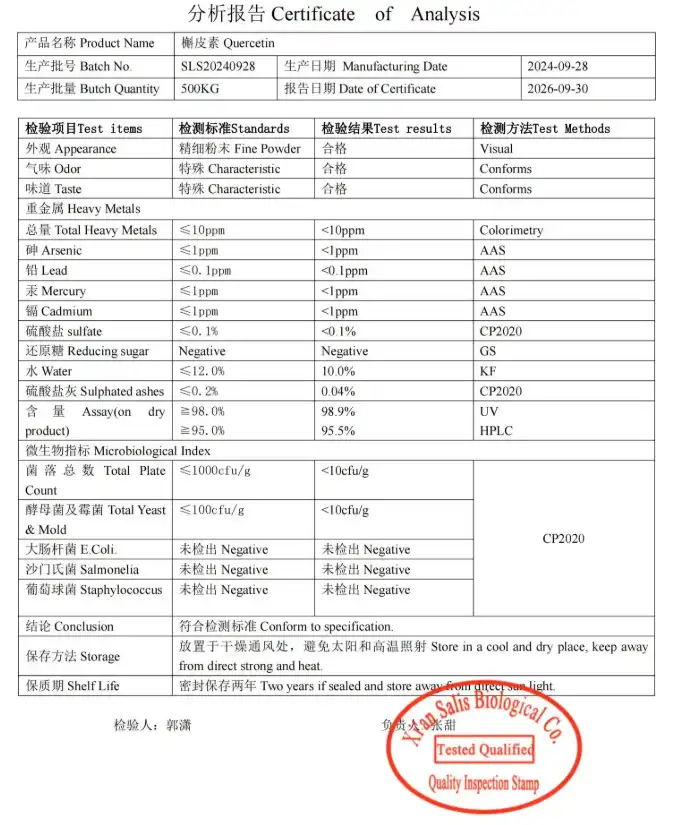
Determining the optimal dosage of quercetin powder for blood pressure control can be challenging, as research in this area is ongoing and individual responses may vary. However, several studies have provided insights into potentially effective dosages.
Many clinical trials investigating quercetin's effects on blood pressure have used dosages ranging from 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day. For instance, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that quercetin supplementation at doses of 500 mg or more per day was associated with significant reductions in blood pressure.
It's worth noting that the bioavailability of quercetin can be relatively low, meaning that not all of the ingested quercetin is absorbed and utilized by the body. To address this, some supplements combine quercetin with other compounds like vitamin C or bromelain, which may enhance its absorption.
When considering quercetin supplementation for blood pressure control, it's crucial to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it if needed. A common starting dose is 500 mg per day, taken in one or two divided doses. Some people may find benefit from higher doses, up to 1,000 mg or even 1,500 mg per day, but these higher doses should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It's also important to consider the form of quercetin being used. Quercetin dihydrate is a common form found in many supplements, but other forms like quercetin aglycone or quercetin glycosides may have different absorption rates and effectiveness.
The duration of supplementation can also play a role in its effectiveness. Some studies have shown benefits after just a few weeks of supplementation, while others suggest that longer-term use may be necessary to see significant effects on blood pressure.
It's crucial to remember that quercetin should not be used as a replacement for prescribed blood pressure medications without consulting a healthcare provider. Additionally, individuals with certain health conditions or those taking specific medications should exercise caution and seek medical advice before starting quercetin supplementation.
Can Quercetin Powder be combined with other supplements for better blood pressure management?
Quercetin powder can indeed be combined with other supplements to potentially enhance its blood pressure-lowering effects or provide complementary benefits for overall cardiovascular health. However, it's essential to approach such combinations with caution and ideally under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
One of the most common combinations is quercetin with vitamin C. This pairing is based on the idea that vitamin C may help improve the bioavailability and effectiveness of quercetin. Some studies have suggested that this combination could lead to better absorption of quercetin in the body, potentially enhancing its blood pressure-lowering effects.
Another popular combination is quercetin with omega-3 fatty acids, particularly from fish oil. Omega-3s are known for their cardiovascular benefits, including potential blood pressure reduction. When combined with quercetin, they may offer synergistic effects for heart health. The anti-inflammatory properties of both quercetin and omega-3s could work together to reduce inflammation in the cardiovascular system, potentially leading to better blood pressure control.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is another supplement that is sometimes combined with quercetin. CoQ10 is involved in energy production in cells and has been studied for its potential cardiovascular benefits, including blood pressure reduction. The combination of quercetin and CoQ10 could potentially offer dual support for heart health.
For those looking to address multiple aspects of cardiovascular health, combining quercetin with a magnesium supplement might be beneficial. Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure and has been shown to have mild blood pressure-lowering effects in some studies.
Moreover, it's essential to remember that supplements should not be seen as a replacement for a healthy lifestyle. Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and other lifestyle factors play crucial roles in managing blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. Supplements like quercetin should be viewed as part of a comprehensive approach to health rather than a standalone solution.
Conclusion
Quercetin powder shows promise as a natural supplement for supporting healthy blood pressure levels. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, along with its potential to enhance nitric oxide production, make it an interesting option for those looking to maintain cardiovascular health. While research is ongoing, current evidence suggests that quercetin may be effective in reducing blood pressure, especially when used as part of a comprehensive approach to heart health.
However, it's crucial to approach quercetin supplementation with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. The optimal dosage can vary depending on individual factors, and combining quercetin with other supplements should be done carefully to avoid potential interactions. As with any supplement, quercetin should not be seen as a replacement for a healthy lifestyle or prescribed medications.
Ultimately, while quercetin powder shows potential in supporting blood pressure management, it's most effective when used as part of a holistic approach to cardiovascular health that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and appropriate medical care.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
References
1. Serban, M. C., et al. (2016). Effects of Quercetin on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Journal of the American Heart Association, 5(7), e002713.
2. Egert, S., et al. (2009). Quercetin reduces systolic blood pressure and plasma oxidised low-density lipoprotein concentrations in overweight subjects with a high-cardiovascular disease risk phenotype: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled cross-over study. British Journal of Nutrition, 102(7), 1065-1074.
3. Edwards, R. L., et al. (2007). Quercetin reduces blood pressure in hypertensive subjects. The Journal of Nutrition, 137(11), 2405-2411.
4. Perez-Vizcaino, F., et al. (2009). Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin. Pharmacological Reports, 61(1), 67-75.
5. Larson, A. J., et al. (2012). Quercetin: A Treatment for Hypertension?—A Review of Efficacy and Mechanisms. Pharmaceuticals, 5(2), 149-156.
6. Brüll, V., et al. (2015). Effects of a quercetin-rich onion skin extract on 24 h ambulatory blood pressure and endothelial function in overweight-to-obese patients with (pre-)hypertension: a randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled cross-over trial. British Journal of Nutrition, 114(8), 1263-1277.
7. Duarte, J., et al. (2001). Antihypertensive effects of the flavonoid quercetin in spontaneously hypertensive rats. British Journal of Pharmacology, 133(1), 117-124.
8. Zahedi, M., et al. (2013). Does quercetin improve cardiovascular risk factors and inflammatory biomarkers in women with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 4(7), 777-785.
9. Lee, K. H., et al. (2011). Mechanisms of Vascular Relaxation Induced by the Citrulline/Nitric Oxide Cycle. Nitric Oxide, 25(1), 65-73.
10. Boots, A. W., et al. (2008). Health effects of quercetin: from antioxidant to nutraceutical. European Journal of Pharmacology, 585(2-3), 325-337.

