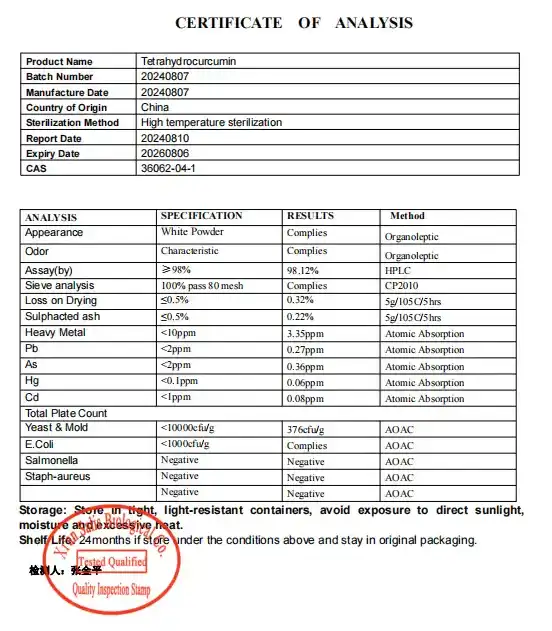
How does the bioavailability of tetrahydrocurcumin compare to curcumin?
One of the most significant differences between Tetrahydrocurcumin Powder and curcumin lies in their bioavailability – the extent to which a substance can be absorbed and utilized by the body. Curcumin, while renowned for its potential health benefits, has long been plagued by poor bioavailability. This limitation is primarily due to its low solubility in water and rapid metabolism in the body, which results in minimal absorption into the bloodstream.
Tetrahydrocurcumin, on the other hand, exhibits superior bioavailability compared to its parent compound. This enhanced absorption is attributed to its chemical structure, which is more stable and resistant to degradation in the digestive tract. Studies have shown that tetrahydrocurcumin can be absorbed up to 5-7 times more efficiently than standard curcumin, allowing for greater concentrations to reach the bloodstream and target tissues.
The improved bioavailability of tetrahydrocurcumin is due to several factors:
- Increased stability: Tetrahydrocurcumin is more stable in the acidic environment of the stomach, reducing degradation before absorption.
- Enhanced solubility: It has better water solubility, facilitating easier absorption through the intestinal lining.
- Reduced metabolism: Tetrahydrocurcumin undergoes less extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, allowing more of the compound to circulate in the body.
These characteristics make tetrahydrocurcumin a promising alternative for those seeking to maximize the potential benefits of curcuminoids. However, it's important to note that bioavailability can still be influenced by various factors, including individual physiology, dietary habits, and the presence of other compounds that may enhance absorption.
What are the key structural differences between tetrahydrocurcumin and curcumin?
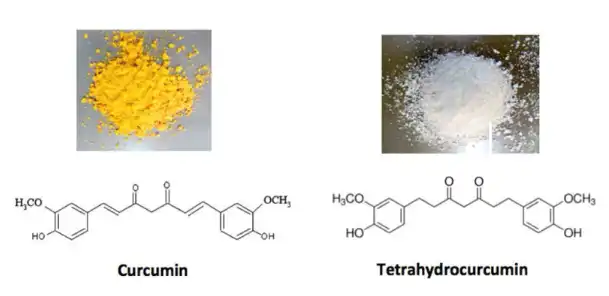
The structural differences between Tetrahydrocurcumin Powder and curcumin are fundamental to understanding their distinct properties and effects in the body. Curcumin is a polyphenolic compound characterized by its bright yellow color and is composed of two phenol rings connected by two α,β-unsaturated carbonyl groups. This structure gives curcumin its potent antioxidant properties but also contributes to its instability and poor bioavailability.
Tetrahydrocurcumin, in contrast, is a metabolite of curcumin that results from the reduction of the double bonds in the heptadiene-3,5-dione structure. This reduction process leads to several key structural changes:
- Saturation of double bonds: The unsaturated bonds in curcumin's central seven-carbon chain are reduced, resulting in a more flexible structure.
- Loss of conjugation: The reduction eliminates the conjugated system present in curcumin, which is responsible for its yellow color.
- Increased polarity: Tetrahydrocurcumin is more polar than curcumin, contributing to its improved water solubility.
These structural modifications have significant implications for the compound's properties:
- Enhanced stability: The saturated structure of tetrahydrocurcumin makes it more resistant to degradation in physiological conditions.
- Improved bioavailability: The increased polarity and flexibility contribute to better absorption and distribution in the body.
- Different reactivity: While both compounds possess antioxidant properties, their mechanisms of action may differ due to the structural changes.
Understanding these structural differences is crucial for researchers and healthcare professionals when considering the potential applications of these compounds. The unique structure of tetrahydrocurcumin may offer advantages in certain therapeutic contexts, particularly where enhanced bioavailability is desired.
How do the health benefits of tetrahydrocurcumin differ from those of curcumin?
While both Tetrahydrocurcumin Powder and curcumin offer potential health benefits, their differing structures and bioavailability profiles lead to some distinctions in their effects on human health. Curcumin has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and potential anti-cancer properties. Tetrahydrocurcumin, as a metabolite of curcumin, shares many of these benefits but may offer some unique advantages due to its enhanced bioavailability and stability.
Antioxidant activity is a key area where tetrahydrocurcumin may outperform curcumin. Studies have shown that tetrahydrocurcumin exhibits stronger antioxidant effects in certain contexts, particularly in lipid peroxidation and free radical scavenging. This enhanced antioxidant capacity could translate to more effective protection against oxidative stress-related conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.
In terms of anti-inflammatory properties, both compounds have demonstrated significant potential. However, the improved bioavailability of tetrahydrocurcumin suggests that it may be more effective at lower doses. This could be particularly beneficial for conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis or inflammatory bowel diseases.
Metabolic health is another area where tetrahydrocurcumin shows promise. Research indicates that it may have superior effects on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity compared to curcumin. This could make tetrahydrocurcumin a valuable compound in the management of diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Cardiovascular health benefits have been observed with both compounds, but tetrahydrocurcumin's enhanced bioavailability may lead to more pronounced effects. Studies have shown its potential in reducing blood pressure, improving lipid profiles, and protecting against atherosclerosis.
While curcumin has been extensively studied for its potential anti-cancer properties, research on tetrahydrocurcumin in this area is still emerging. Some studies suggest that tetrahydrocurcumin may have comparable or even enhanced anti-cancer effects due to its improved bioavailability and unique structural properties.
It's important to note that while Tetrahydrocurcumin Powder offers several advantages over curcumin, both compounds have their place in potential therapeutic applications. The choice between the two may depend on specific health goals, individual physiology, and the particular condition being addressed. As research in this field continues to evolve, a more comprehensive understanding of the distinct benefits of tetrahydrocurcumin and curcumin will emerge, allowing for more targeted and effective use of these promising natural compounds.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.