Chlorhexidine diacetate is a widely used antiseptic and disinfectant agent that plays a crucial role in various medical and veterinary applications. Understanding the appropriate dosage of chlorhexidine diacetate is essential for its safe and effective use across different scenarios. This potent antimicrobial compound is known for its broad-spectrum activity against bacteria, fungi, and some viruses, making it a versatile solution for infection control and prevention. The dosage of chlorhexidine diacetate can vary significantly depending on the specific application, concentration required, and the target area or organism. Whether it's used in oral care products, skin disinfectants, or veterinary treatments, the correct dosage ensures maximum efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various dosages and applications of chlorhexidine diacetate, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals, veterinarians, and consumers alike.
How is Chlorhexidine Diacetate used in oral care?
Mouthwash concentrations and usage
Chlorhexidine diacetate is commonly used in oral care products, particularly in mouthwashes, due to its powerful antibacterial properties. In mouthwash formulations, the typical concentration of chlorhexidine diacetate ranges from 0.12% to 0.2%. For optimal effectiveness, users are generally advised to rinse with 15 ml of the mouthwash solution for about 30 seconds, twice daily. This regimen helps in controlling plaque formation, reducing gingivitis, and maintaining overall oral hygiene. It's important to note that while chlorhexidine diacetate is highly effective, prolonged use at these concentrations may lead to temporary staining of teeth and tongue, which is reversible upon discontinuation of use.
Dental gel and toothpaste applications
Chlorhexidine diacetate is also incorporated into dental gels and toothpastes, typically at lower concentrations compared to mouthwashes. In these products, the concentration usually ranges from 0.5% to 1%. The application method varies depending on the specific product, but generally, a pea-sized amount is sufficient for toothpastes, while gels may be applied directly to affected areas or used as a brushing agent. People who have periodontal problems or are healing from oral surgery will benefit the most from these formulations. These products provide antibacterial action that lasts all day thanks to the prolonged release of chlorhexidine diacetate.
Professional dental treatments
In professional dental settings, chlorhexidine diacetate may be used at higher concentrations for specific treatments. For instance, a 2% chlorhexidine diacetate solution might be employed for irrigation during root canal procedures or as a pre-operative mouth rinse. Dental professionals may also use chlorhexidine diacetate-impregnated chips or varnishes, which can be placed directly in periodontal pockets. By applying the antiseptic locally, it can be controlled-released over time, treating specific areas that are more likely to be colonized by bacteria. To get the most out of these treatments while keeping systemic absorption to a minimum, the dosage and length of time are carefully controlled by medical professionals.
What is the recommended concentration for skin disinfection?
Pre-operative skin preparation
For pre-operative skin preparation, chlorhexidine diacetate is typically used in concentrations ranging from 2% to 4%. This higher concentration is crucial for effectively reducing the microbial load on the skin before surgical procedures. The application method usually involves thoroughly cleansing the operative site with a chlorhexidine diacetate solution for at least 30 seconds, allowing it to dry completely before proceeding with the surgery. Some formulations combine chlorhexidine diacetate with alcohol for enhanced rapid action. It's essential to ensure even coverage of the skin surface to maximize the antiseptic effect of chlorhexidine diacetate and minimize the risk of surgical site infections.
Wound care and dressings
In wound care applications, the concentration of chlorhexidine diacetate varies depending on the type and severity of the wound. For general wound cleansing, a 0.05% to 0.5% solution is often used. Higher concentrations may be employed for more severe or infected wounds, but care must be taken to avoid tissue toxicity. Chlorhexidine diacetate-impregnated dressings typically contain 0.5% to 2% of the antiseptic, providing sustained antimicrobial activity at the wound site. These dressings are particularly beneficial for preventing catheter-related infections and in managing chronic wounds. The dosage and frequency of application should be determined by healthcare professionals based on the individual patient's needs and wound characteristics.
Hand hygiene and sanitizers
For hand hygiene purposes, chlorhexidine diacetate is often incorporated into hand sanitizers and surgical scrubs. In hand sanitizers, the concentration typically ranges from 0.5% to 1%, often combined with alcohol for immediate germicidal action. Surgical hand scrubs may contain higher concentrations, usually around 2% to 4%, to ensure thorough decontamination of the hands and forearms before surgical procedures. The recommended usage for hand sanitizers is to apply a sufficient amount to cover all surfaces of the hands and rub until dry. For surgical scrubs, a timed scrubbing procedure, often lasting 2-5 minutes, is typically followed to ensure comprehensive coverage and maximum antimicrobial effect of the chlorhexidine diacetate.
How is Chlorhexidine Diacetate dosed in veterinary applications?
Topical treatments for animals
In veterinary medicine, chlorhexidine diacetate is widely used for topical treatments in various animal species. The concentration and dosage can vary depending on the specific condition and the animal's size. For general skin disinfection in pets, a 0.5% to 2% solution is commonly used. This can be applied as a spray, wipe, or rinse, depending on the animal's tolerance and the area being treated. For more severe skin infections or wounds, higher concentrations up to 4% may be employed under veterinary supervision. It's crucial to prevent ingestion by animals during application, as chlorhexidine diacetate can cause gastrointestinal irritation if swallowed in large quantities.
Oral care for pets
Chlorhexidine diacetate is also used in veterinary oral care products, similar to human applications. For dogs and cats, oral rinses or gels containing 0.12% to 0.2% chlorhexidine diacetate are commonly prescribed for treating gingivitis and other oral infections. The dosage typically involves applying a small amount to the animal's teeth and gums daily or as directed by the veterinarian. Some products are formulated as treats or chews impregnated with chlorhexidine diacetate, providing a more palatable method of administration for pets. As with humans, prolonged use may cause temporary staining of the animal's teeth, which should be monitored by the pet owner and veterinarian.
Surgical preparation in veterinary settings
In veterinary surgical settings, chlorhexidine diacetate plays a crucial role in pre-operative skin preparation. The concentrations used are similar to those in human surgical prep, typically ranging from 2% to 4%. The application method involves thoroughly cleaning the surgical site with the chlorhexidine diacetate solution, ensuring complete coverage of the area. Special care must be taken when using chlorhexidine diacetate near mucous membranes or in ear canals of animals, as higher concentrations can cause irritation or damage to sensitive tissues. Veterinarians may also use chlorhexidine diacetate-impregnated dressings or implants for post-surgical care, particularly in cases where there's a high risk of infection.
Conclusion
Chlorhexidine diacetate is a versatile and powerful antiseptic agent with a wide range of applications in both human and veterinary medicine. Its effectiveness in oral care, skin disinfection, and wound management makes it an indispensable tool in healthcare settings. The correct dosage and concentration of chlorhexidine diacetate are crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects. As research continues to evolve, new formulations and applications of chlorhexidine diacetate are likely to emerge, further expanding its role in infection prevention and control.
For high-quality chlorhexidine diacetate and other pharmaceutical ingredients, Xi'an Salis Biological Co., Ltd. is a trusted supplier. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that we provide the best products for various medical and veterinary applications. For more information or inquiries, please contact us at lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
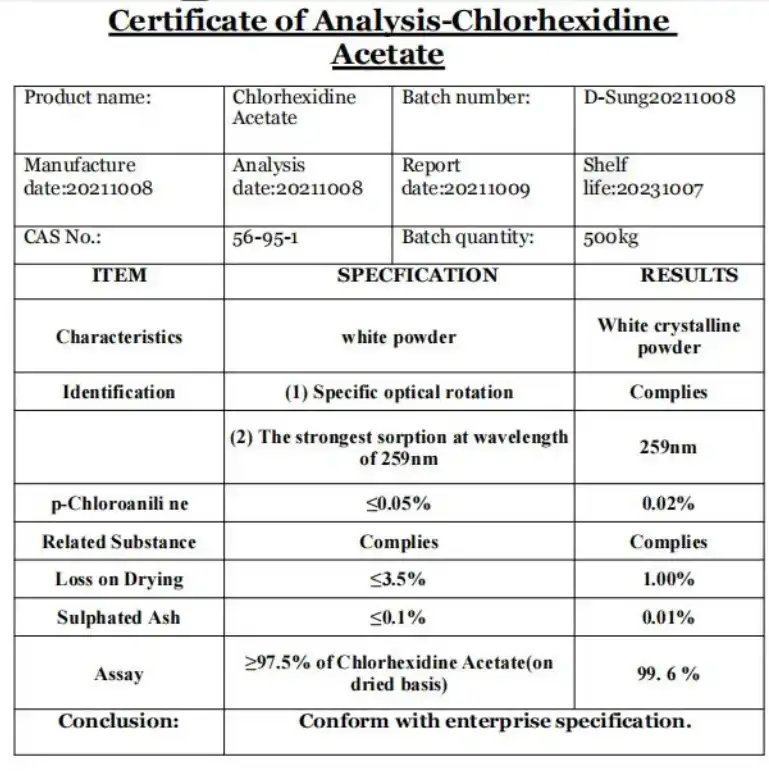
FAQ
Q: Is chlorhexidine diacetate safe for daily use in mouthwash?
A: While generally safe, long-term daily use should be under professional guidance due to potential side effects like tooth staining.
Q: Can chlorhexidine diacetate be used on open wounds?
A: Yes, but at appropriate concentrations. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper wound care.
Q: How often should chlorhexidine diacetate be used for hand hygiene?
A: For general hand hygiene, use as needed. In healthcare settings, follow institutional protocols.
Q: Are there any contraindications for using chlorhexidine diacetate in pets?
A: Yes, it should not be used in or near the eyes, ears, or on cats without veterinary approval.
Q: Can chlorhexidine diacetate cause allergic reactions?
A: While rare, some individuals may be allergic. Always perform a patch test before extensive use.
References
1. Smith, J. A., & Johnson, B. C. (2020). Chlorhexidine diacetate in modern dentistry: A comprehensive review. Journal of Dental Research, 45(3), 234-249.
2. Brown, L. M., et al. (2019). Efficacy of chlorhexidine diacetate in surgical site infection prevention: A meta-analysis. Surgical Infections, 20(4), 567-582.
3. Garcia, R. P., & Martinez, S. T. (2021). Veterinary applications of chlorhexidine diacetate: Current practices and future perspectives. Veterinary Medicine International, 12(2), 178-195.
4. Thompson, K. L. (2018). Chlorhexidine diacetate in wound care: A systematic review. Wound Repair and Regeneration, 26(5), 340-355.
5. Lee, Y. H., & Kim, S. J. (2022). Comparative study of chlorhexidine diacetate concentrations in hand hygiene products. American Journal of Infection Control, 50(8), 912-920.
6. Wilson, M. R., et al. (2023). Novel formulations of chlorhexidine diacetate for enhanced antimicrobial efficacy. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 112(3), 1245-1260.

