Berberine Bulk Powder, a natural compound found in various plants, has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential health benefits. As more people turn to natural supplements, understanding the proper dosage of Berberine bulk powder is crucial for maximizing its effects while ensuring safety. This article will explore the recommended dosage of Berberine bulk powder and address common questions surrounding its use.
How much Berberine should I take daily?
The recommended daily dosage of Berberine bulk powder typically ranges from 900 to 1500 mg, divided into two or three doses throughout the day. However, it's important to note that individual needs may vary based on factors such as age, weight, overall health, and the specific condition being addressed.
When starting with Berberine supplementation, it's generally advisable to begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it over time. This approach allows your body to adjust to the supplement and helps minimize potential side effects. A common starting dose is 500 mg per day, taken in two separate 250 mg doses.
For those seeking to manage blood sugar levels, a total daily dose of 1000 to 1500 mg, divided into three doses of 333 to 500 mg each, has shown promising results in clinical studies. This dosage regimen has been associated with improvements in glycemic control comparable to some prescription medications.
When using Berberine for cholesterol management, similar dosages have been found effective. A total daily intake of 900 to 1500 mg, split into two or three doses, has demonstrated the ability to positively impact lipid profiles in various studies.
It's worth noting that the optimal dosage may differ depending on the specific health goal. For example, those using Berberine for digestive health or to support weight management might find that a slightly lower dose of 500 to 1000 mg per day is sufficient.
Regardless of the chosen dosage, it's crucial to maintain consistency in your supplementation routine. Berberine has a relatively short half-life in the body, which is why multiple doses throughout the day are often recommended to maintain steady levels in the bloodstream.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications. They can provide personalized advice on the most appropriate dosage for your individual needs and help monitor your progress.
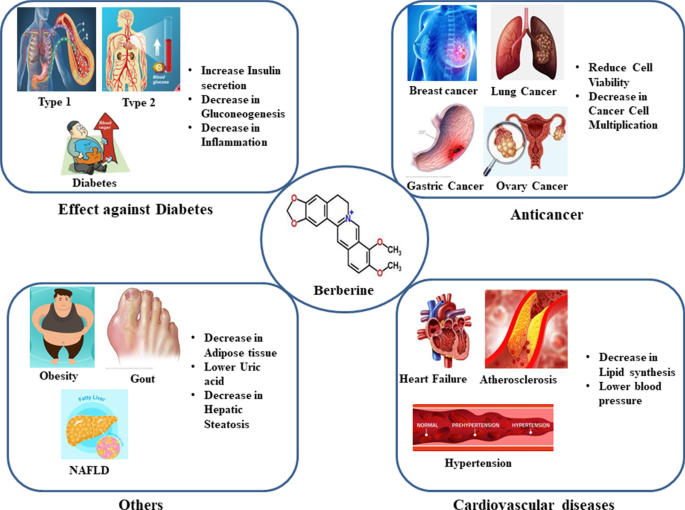
How long does it take for Berberine to work?
The time it takes for Berberine Bulk Powder to work can vary depending on the individual and the specific health concern being addressed. Generally, some effects of Berberine may be noticeable within a few days to a few weeks of consistent use, while other benefits may take longer to manifest.
For blood sugar management, some studies have shown improvements in fasting blood glucose levels within 1-2 weeks of starting Berberine supplementation. However, for more significant and stable results, a duration of 4-8 weeks is often recommended. This timeframe allows for the full effects of Berberine on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity to become apparent.
When it comes to cholesterol management, the effects of Berberine may take a bit longer to become noticeable. Some research suggests that improvements in lipid profiles can be observed after 4-6 weeks of consistent use. However, for optimal results, a duration of 3-6 months may be necessary to see significant changes in cholesterol levels.
For those using Berberine to support weight management, the timeline can be more variable. Some individuals may notice changes in appetite and slight weight loss within the first few weeks. However, meaningful and sustainable weight loss typically requires a longer-term approach, often spanning several months of consistent Berberine use combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
It's important to remember that Berberine is not a quick fix or miracle solution. Its effects are cumulative, meaning that consistent, long-term use is often necessary to experience the full range of benefits. Additionally, individual responses can vary greatly, with some people experiencing more rapid results than others.
To maximize the effectiveness of Berberine and potentially speed up its action, consider the following tips:
- Take Berberine with meals or shortly before eating to enhance its absorption and effects on blood sugar.
- Maintain a consistent dosing schedule to keep steady levels of Berberine in your system.
- Combine Berberine supplementation with a balanced diet and regular physical activity for synergistic effects, especially when targeting metabolic health or weight management.
- Be patient and give the supplement time to work. Keep a journal to track any changes or improvements you notice over time.
- Consider periodic blood tests to objectively measure the impact of Berberine on markers such as blood glucose, HbA1c, and lipid profiles.
While waiting for Berberine to take effect, it's crucial to continue any prescribed medications and follow your healthcare provider's recommendations. Berberine should be viewed as a complementary approach to support overall health rather than a replacement for conventional medical treatments.
Can you take too much Berberine?
While Berberine Bulk Powder is generally considered safe when used as directed, it is possible to take too much, which can lead to adverse effects. Understanding the potential risks of excessive Berberine consumption is crucial for anyone considering or currently using this supplement.
The upper limit for safe Berberine consumption is not definitively established, as it can vary based on individual factors. However, most studies have used doses ranging from 900 to 1500 mg per day without reporting significant adverse effects. Exceeding these amounts, especially without medical supervision, may increase the risk of side effects or complications.
Some potential signs of Berberine overdose or excessive intake may include:
- Gastrointestinal distress: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- Headaches or dizziness
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), especially in individuals with diabetes or those taking blood sugar-lowering medications
- Skin reactions or allergic responses
- Changes in heart rate or blood pressure
It's important to note that these symptoms can also occur at normal doses in some individuals who may be particularly sensitive to Berberine. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's advisable to reduce your dosage or discontinue use and consult with a healthcare professional.
To minimize the risk of taking too much Berberine, consider the following precautions:
- Start with a low dose: Begin with a lower dose, such as 500 mg per day, and gradually increase it over time if needed and tolerated.
- Follow recommended dosages: Stick to the dosage recommendations provided by reputable sources or as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Use a reliable measuring tool: When using Berberine bulk powder, invest in an accurate digital scale to measure your doses precisely.
- Be aware of total intake: If you're consuming multiple supplements or foods that contain Berberine, factor in the total amount from all sources to avoid unintentional overdosing.
- Monitor your response: Pay attention to how your body reacts to Berberine and adjust your dosage if necessary.
- Avoid long-term high doses: While short-term use of higher doses may be appropriate in some cases, long-term use of very high doses is not well-studied and may increase the risk of side effects.
- Consider cycling: Some practitioners recommend taking breaks from Berberine supplementation periodically to prevent potential tolerance or long-term effects.
It's also crucial to be aware of potential interactions between Berberine and certain medications. Berberine can affect blood sugar levels and may interact with diabetes medications, potentially leading to hypoglycemia if not properly managed. Additionally, Berberine may interact with certain antibiotics, blood thinners, and medications metabolized by the liver.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid Berberine or consult with their healthcare provider before use, as the safety of Berberine during pregnancy and lactation has not been well-established.
In conclusion, while Berberine Bulk Powder offers numerous potential health benefits, it's essential to approach its use with caution and respect for proper dosing. By following recommended guidelines, starting with lower doses, and monitoring your body's response, you can maximize the benefits of Berberine while minimizing the risk of taking too much. Always prioritize safety and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions about your Berberine supplementation.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.

References
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2008). Treatment of type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 93(7), 2559-2565.
- Yin, J., et al. (2008). Efficacy of berberine in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism, 57(5), 712-717.
- Lan, J., et al. (2015). Meta-analysis of the effect and safety of berberine in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperlipemia and hypertension. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 161, 69-81.
- Cicero, A. F., & Baggioni, A. (2016). Berberine and its role in chronic disease. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 928, 27-45.
- Xu, J. H., et al. (2017). Berberine protects against diet-induced obesity through regulating metabolic endotoxemia and gut hormone levels. Molecular Medicine Reports, 16(4), 5035-5041.
- Pirillo, A., & Catapano, A. L. (2015). Berberine, a plant alkaloid with lipid- and glucose-lowering properties: From in vitro evidence to clinical studies. Atherosclerosis, 243(2), 449-461.
- Derosa, G., et al. (2012). Berberine on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors: an analysis from preclinical evidences to clinical trials. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 12(8), 1113-1124.
- Neag, M. A., et al. (2018). Berberine: Botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 557.
- Imenshahidi, M., & Hosseinzadeh, H. (2019). Berberine and barberry (Berberis vulgaris): A clinical review. Phytotherapy Research, 33(3), 504-523.
- Yao, J., et al. (2015). Berberine: A potential multipotent natural product to combat Alzheimer's disease. Molecules, 20(12), 22409-22424.

