Genistein powder, derived from soybeans and other legumes, is a popular dietary supplement known for its potential health benefits. As an isoflavone, genistein has garnered attention for its antioxidant properties and potential role in supporting various aspects of health. However, determining the appropriate dosage of genistein powder can be challenging, as it may vary depending on individual factors and the intended purpose of supplementation. In this article, we'll explore the recommended dosage of genistein powder and address some common questions related to its use.

How does genistein powder dosage vary for different health conditions?
The recommended dosage of genistein powder can vary significantly depending on the specific health condition being addressed. Research has shown that different amounts of genistein may be beneficial for various health concerns. Here's a breakdown of some common health conditions and the associated genistein dosages:
- Menopausal symptoms: For women experiencing menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats, studies have used genistein doses ranging from 30 to 60 mg per day. Some research suggests that a dose of 54 mg of genistein daily may be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of hot flashes.
- Bone health: To support bone health and potentially reduce the risk of osteoporosis, studies have used genistein doses between 54 and 108 mg per day. A dose of 54 mg daily has been shown to improve bone mineral density in postmenopausal women.
- Cardiovascular health: For potential cardiovascular benefits, such as improving lipid profiles and reducing inflammation, studies have used genistein doses ranging from 30 to 120 mg per day. Some research suggests that a dose of 54 mg daily may help improve markers of cardiovascular health.
- Cancer prevention: While more research is needed, some studies investigating the potential anti-cancer properties of genistein have used doses ranging from 30 to 300 mg per day. However, it's important to note that high doses of genistein should only be taken under medical supervision, as they may interact with certain cancer treatments.
- Skin health: For potential skin benefits, such as improving skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles, some studies have used topical genistein preparations containing 0.5% to 1% genistein. When taken orally for skin health, doses of 40 to 60 mg per day have been used in research.
It's crucial to remember that these dosages are based on research studies and may not be appropriate for everyone. Factors such as age, weight, overall health, and potential interactions with medications should be considered when determining the appropriate genistein powder dosage. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Are there different recommended dosages for men and women?
When it comes to genistein powder supplementation, there can indeed be differences in the recommended dosages for men and women. These variations are primarily due to the different physiological needs and potential effects of genistein on hormone-sensitive conditions. Let's explore the dosage recommendations for both genders:
Dosage recommendations for women:
Women, particularly those in menopause or post-menopause, have been the focus of many genistein studies. As a result, dosage recommendations for women are often more clearly defined:
- Menopausal symptoms: As mentioned earlier, doses of 30 to 60 mg per day have been used in studies focusing on alleviating menopausal symptoms. The most commonly recommended dose is 54 mg daily.
- Bone health: For postmenopausal women concerned about bone health, doses of 54 to 108 mg per day have been studied. A daily dose of 54 mg has shown promising results in improving bone mineral density.
- General health: For women looking to incorporate genistein as a general health supplement, a lower dose of 20 to 30 mg per day may be sufficient.
It's important to note that women with a history of hormone-sensitive cancers, such as breast cancer, should consult their healthcare provider before taking genistein supplements, as its effects on these conditions are not fully understood.
Dosage recommendations for men:
While there has been less research focused specifically on genistein supplementation in men, some studies have explored its potential benefits:
- Prostate health: Some studies have investigated the potential benefits of genistein for prostate health, using doses ranging from 30 to 60 mg per day.
- Cardiovascular health: For potential cardiovascular benefits in men, doses similar to those used in women (30 to 120 mg per day) have been studied.
- General health: As with women, men looking to use genistein as a general health supplement may consider a lower dose of 20 to 30 mg per day.
It's worth noting that some concerns have been raised about the potential effects of high doses of genistein on male fertility and hormone balance. While research in this area is ongoing, men should be cautious about using high doses of genistein without medical supervision.
Ultimately, the appropriate dosage of genistein powder may vary between individuals, regardless of gender. Factors such as age, overall health, and specific health goals should be considered when determining the right dose. It's always recommended to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it if needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
How long does it take for genistein powder to show effects?
The time it takes for genistein powder to show effects can vary depending on several factors, including the specific health condition being addressed, the dosage used, and individual differences in metabolism and absorption. Understanding the timeline for potential benefits can help set realistic expectations when incorporating genistein powder into your health regimen. Let's explore the typical timeframes for various health effects:
Short-term effects (within days to weeks):
- Antioxidant activity: Genistein's antioxidant properties may begin to take effect relatively quickly, potentially within days of starting supplementation. However, measurable changes in oxidative stress markers may take several weeks to become apparent.
- Menopausal symptoms: Some women report improvements in hot flashes and night sweats within 2-4 weeks of starting genistein supplementation. However, optimal effects may not be seen until 12 weeks or more of consistent use.
- Inflammatory markers: Changes in inflammatory markers may be detectable within 4-8 weeks of starting genistein supplementation, although the clinical significance of these changes may take longer to manifest.
Medium-term effects (within months):
- Bone health: Improvements in bone mineral density and markers of bone metabolism may begin to be detectable after 3-6 months of consistent genistein supplementation. However, significant changes in bone density typically require longer-term use.
- Cardiovascular health: Changes in lipid profiles and other cardiovascular risk factors may become apparent after 3-6 months of genistein use. Some studies have shown improvements in cholesterol levels and blood pressure within this timeframe.
- Skin health: When used topically or orally for skin health, improvements in skin elasticity and reduction in wrinkles may become noticeable after 2-3 months of consistent use.
Long-term effects (6 months and beyond):
- Bone density: Significant improvements in bone mineral density typically require long-term use of genistein, with some studies showing benefits after 1-2 years of consistent supplementation.
- Cancer prevention: The potential cancer-preventive effects of genistein are thought to be cumulative over time. Long-term studies looking at cancer risk reduction have often followed participants for several years.
- Cognitive function: Some research suggests that long-term consumption of genistein and other isoflavones may have beneficial effects on cognitive function, particularly in postmenopausal women. These effects may take years to become apparent.
It's important to note that individual responses to genistein powder can vary significantly. Some people may experience noticeable effects more quickly, while others may take longer to see benefits. Additionally, the effects of genistein may be subtle and not immediately apparent without specific testing or measurements.
To maximize the potential benefits of genistein powder, consistent use over time is typically recommended. It's also crucial to combine supplementation with a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor any changes and ensure that the supplementation is having the desired effects.
Remember that while genistein powder may offer various health benefits, it should not be considered a magic solution or a replacement for medical treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the recommended dosage of genistein powder can vary depending on the specific health condition being addressed, as well as individual factors such as age, gender, and overall health. While general dosage ranges have been established through research, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate dosage for your individual needs. By understanding the potential effects and timeline of genistein supplementation, you can make informed decisions about incorporating this isoflavone into your health regimen. Remember that consistency and patience are key when using natural supplements like genistein powder, as many of its benefits may take time to become apparent.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact lea_slsbio@163.com,WhatsApp+86 13193326505.
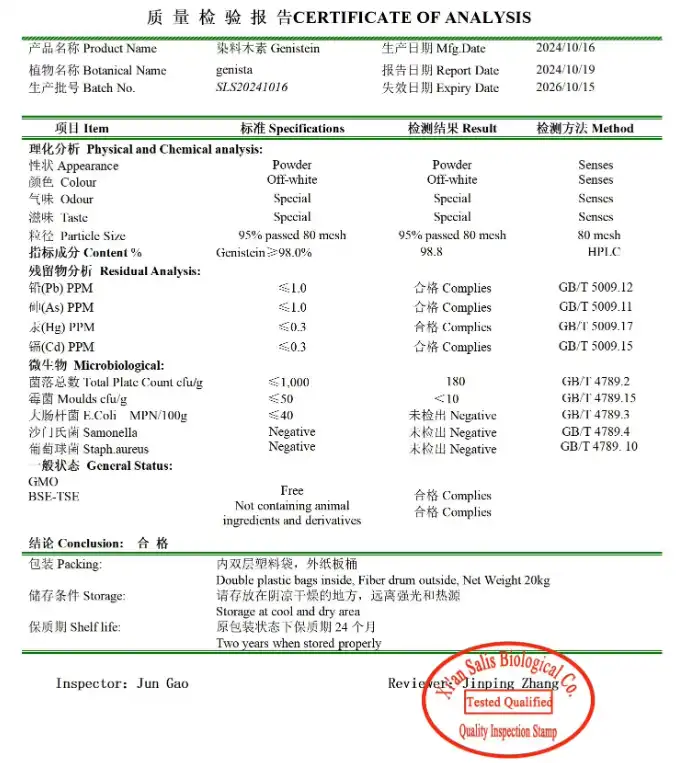
References
1. Marini H, et al. (2007). Effects of the phytoestrogen genistein on bone metabolism in osteopenic postmenopausal women: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine, 146(12), 839-847.
2. Squadrito F, et al. (2013). The effect of genistein on cardiovascular risk factors in postmenopausal women: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Climacteric, 16(6), 684-699.
3. Messina M. (2014). Soy foods, isoflavones, and the health of postmenopausal women. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 100(Supplement 1), 423S-430S.
4. Spagnuolo C, et al. (2015). Genistein and cancer: current status, challenges, and future directions. Advances in Nutrition, 6(4), 408-419.
5. Bitto A, et al. (2010). Genistein aglycone: a new therapeutic approach to reduce endometrial hyperplasia. Phytomedicine, 17(11), 844-850.
6. Polkowski K & Mazurek AP. (2000). Biological properties of genistein. A review of in vitro and in vivo data. Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica, 57(2), 135-155.
7. Ganai AA & Farooqi H. (2015). Bioactivity of genistein: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 76, 30-38.
8. Morabito N, et al. (2002). Effects of genistein and hormone-replacement therapy on bone loss in early postmenopausal women: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 17(10), 1904-1912.
9. Cassidy A. (2003). Potential risks and benefits of phytoestrogen-rich diets. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research, 73(2), 120-126.
10. Setchell KD & Cassidy A. (1999). Dietary isoflavones: biological effects and relevance to human health. The Journal of Nutrition, 129(3), 758S-767S.

