How does Tirzepatide powder compare to other diabetes medications?
Tirzepatide powder represents a significant advancement in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Unlike traditional diabetes medications that target only one metabolic pathway, Tirzepatide acts on both the GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptors. This dual action provides a more comprehensive approach to managing blood glucose levels and promoting weight loss.

Compared to other diabetes medications, Tirzepatide has shown remarkable efficacy in clinical trials. In head-to-head studies, it has outperformed popular GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and dulaglutide in terms of both glycemic control and weight reduction. For instance, in the SURPASS-2 trial, Tirzepatide demonstrated superior HbA1c reduction and weight loss compared to semaglutide, with patients achieving up to 2.3% reduction in HbA1c and 12.4 kg weight loss at the highest dose.
Moreover, Tirzepatide's unique mechanism of action may offer additional benefits beyond glucose control and weight loss. Preclinical studies suggest that it may have positive effects on cardiovascular health, lipid profiles, and even cognitive function. These potential advantages make Tirzepatide an exciting option for patients who have not achieved adequate control with other diabetes medications or who are looking for a more comprehensive treatment approach.
It's important to note that while Tirzepatide shows promise, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The choice of diabetes medication should always be made in consultation with a healthcare provider, taking into account individual patient factors such as medical history, comorbidities, and treatment goals. As research on Tirzepatide continues, we may gain further insights into its long-term efficacy and safety profile, which will help inform its place in diabetes management strategies.
What factors influence the dosage of Tirzepatide powder?
Determining the appropriate dosage of Tirzepatide powder is a complex process that takes into account several important factors. Healthcare providers carefully consider these elements to ensure that patients receive the most effective and safe treatment regimen. Let's explore some of the key factors that influence the dosage of Tirzepatide powder:
- Patient's medical history: The individual's overall health status, including any pre-existing medical conditions, plays a crucial role in determining the initial dosage. Patients with a history of gastrointestinal issues or pancreatitis, for example, may require a more cautious approach to dosing.
- Severity of diabetes: The degree of glycemic control and the duration of diabetes can impact the dosage. Patients with more severe or long-standing diabetes may require higher doses to achieve optimal blood glucose management.
- Body weight: As Tirzepatide is known for its weight loss effects, the patient's current body weight and weight loss goals may influence the dosing strategy. Higher doses have been associated with greater weight reduction in clinical trials.
- Kidney function: Renal impairment can affect drug metabolism and excretion. Patients with reduced kidney function may require dose adjustments to prevent potential complications.
- Concomitant medications: The use of other medications, particularly those that affect blood glucose levels or interact with Tirzepatide, may necessitate dosage modifications.
- Treatment response: As patients begin therapy, their response to Tirzepatide in terms of glycemic control and tolerability will guide subsequent dosage adjustments.
- Age: Elderly patients may metabolize medications differently and may be more susceptible to side effects, potentially requiring a more conservative dosing approach.
- Gastrointestinal tolerance: Since Tirzepatide can cause gastrointestinal side effects, especially during initiation, the dosage may be titrated slowly to improve tolerability.
It's crucial to understand that the dosage of Tirzepatide powder is not static and may change over time. Healthcare providers typically start with a lower dose and gradually increase it based on the patient's response and tolerability. This approach, known as dose titration, allows for personalized treatment optimization while minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, HbA1c, body weight, and other relevant clinical parameters is essential for assessing the effectiveness of the current dosage and making informed decisions about potential adjustments. Patients should maintain open communication with their healthcare providers and report any changes in their condition or the emergence of side effects promptly.
As research on Tirzepatide continues, our understanding of optimal dosing strategies may evolve. Future studies may provide insights into more refined dosing algorithms that take into account additional factors such as genetic markers or specific comorbidities. This ongoing research underscores the importance of staying informed about the latest developments in Tirzepatide therapy and working closely with healthcare providers to ensure the most appropriate and effective treatment plan.
Can the dosage of Tirzepatide powder be adjusted over time?
Yes, the dosage of Tirzepatide powder can and often should be adjusted over time. Dose adjustment is a crucial aspect of managing treatment with Tirzepatide, as it allows healthcare providers to optimize the medication's efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. The process of adjusting the dosage is typically referred to as dose titration, and it plays a significant role in achieving the best possible outcomes for patients using Tirzepatide.
The initial dosage of Tirzepatide powder is generally lower than the target therapeutic dose. This conservative approach serves several purposes:
- It allows the patient's body to acclimate to the medication gradually, reducing the likelihood of severe side effects.
- It helps healthcare providers assess the patient's individual response to the drug.
- It provides an opportunity to identify any potential adverse reactions early in the treatment process.
As treatment progresses, the dosage may be incrementally increased based on several factors:
- Glycemic control: If blood glucose levels remain above target ranges, the dosage may be increased to improve glycemic control.
- Weight loss progress: For patients using Tirzepatide for weight management, the dosage might be adjusted to optimize weight loss outcomes.
- Tolerability: If the patient experiences minimal side effects, the dose may be increased more rapidly to reach the target therapeutic level.
- Individual response: Some patients may show significant improvements at lower doses, while others may require higher doses to achieve desired results.
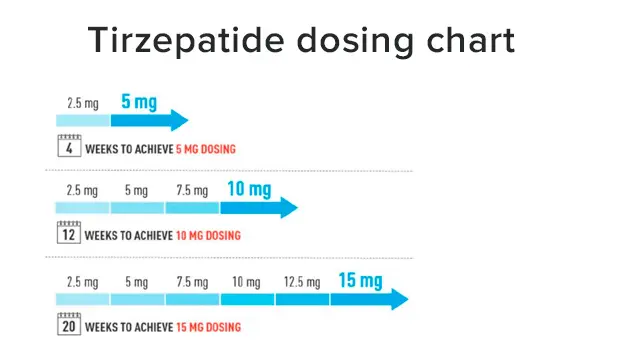
The typical titration schedule for Tirzepatide, as observed in clinical trials and recommended by manufacturers, often follows a pattern of dose increases every 4 weeks. For example, a common titration schedule might look like this:
- Weeks 1-4: 2.5 mg once weekly
- Weeks 5-8: 5 mg once weekly
- Weeks 9-12: 7.5 mg once weekly
- Weeks 13 and beyond: 10 mg once weekly (if needed and tolerated)
It's important to note that this is a general guideline, and actual titration schedules may vary based on individual patient factors and healthcare provider discretion. Some patients may require a slower titration process, while others may be able to progress more quickly.
Long-term use of Tirzepatide may also necessitate dosage adjustments. Factors that could influence long-term dosage changes include:
- Changes in body weight: As patients lose weight, their insulin sensitivity may improve, potentially allowing for dose reductions.
- Alterations in lifestyle: Significant changes in diet or exercise habits may affect glucose metabolism and require dosage adjustments.
- Development of comorbidities: The onset of new health conditions or changes in existing ones may necessitate dosage modifications.
- Aging: As patients age, their metabolism and drug tolerance may change, requiring dosage reconsideration.
Throughout the course of treatment with Tirzepatide powder, regular monitoring is essential. This typically includes:
- Frequent blood glucose measurements
- Periodic HbA1c tests
- Regular weight checks
- Assessment of kidney function
- Monitoring for potential side effects
These monitoring practices allow healthcare providers to make informed decisions about dosage adjustments and ensure that the treatment remains safe and effective over time.
It's crucial for patients to adhere to their prescribed dosage and schedule, and to never adjust their dosage without consulting their healthcare provider. Self-adjustment of Tirzepatide dosage can lead to suboptimal treatment outcomes or increase the risk of adverse effects.
In conclusion, the ability to adjust the dosage of Tirzepatide powder over time is a valuable feature of this medication. It allows for personalized treatment that can be fine-tuned to meet each patient's unique needs and response patterns. By working closely with healthcare providers and maintaining open communication about treatment progress and any side effects, patients can benefit from a dynamic and responsive approach to Tirzepatide therapy, maximizing its potential benefits in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References
- Frías JP, et al. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021;
- Rosenstock J, et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;
- Ludvik B, et al. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;
- Del Prato S, et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;
- Dahl D, et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Tirzepatide vs Placebo Added to Titrated Insulin Glargine on Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS-5 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2022;
- Frías JP, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;
- Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;
- Min T, Bain SC. The Role of Tirzepatide, Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: The SURPASS Clinical Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2021;
- Nauck MA, Quast DR, Wefers J, Meier JJ. GIP and GLP-1 in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and obesity: potential therapeutic targets? Diabetologia. 2021;
- Coskun T, et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol Metab. 2018;

