Amoxicillin Powder is a widely prescribed antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. It's essential to take this medication as directed by your healthcare provider to ensure its effectiveness. However, there may be instances when you forget to take a dose. If you find yourself in this situation, it's important to know how to proceed to maintain the effectiveness of your treatment.
How long after a missed dose can I take Amoxicillin?
If you realize you've missed a dose of Amoxicillin Powder, the timing of your next action depends on how much time has passed since the missed dose. Generally, if you remember within a few hours of the scheduled dose, it's usually safe to take it as soon as you recall. However, if it's close to the time for your next scheduled dose, it's best to skip the missed dose and continue with your regular dosing schedule.
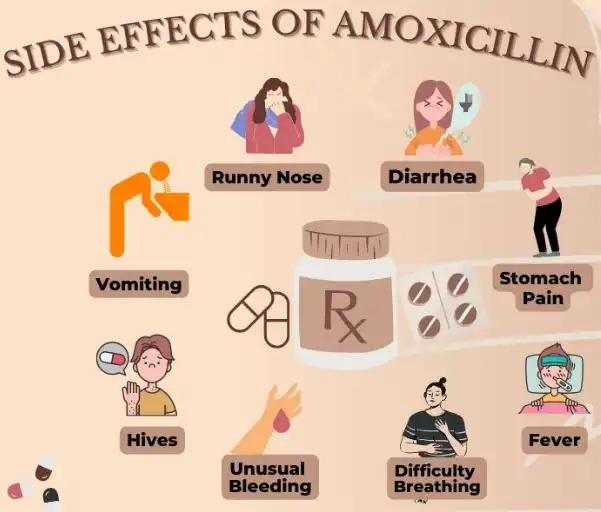
The specific window for taking a missed dose can vary depending on your prescribed dosing frequency. For instance:
- If you're taking Amoxicillin twice a day (every 12 hours), you can take the missed dose if you remember within 6 hours of the scheduled time.
- For a three-times-a-day regimen (every 8 hours), you have about a 4-hour window to take the missed dose.
- If you're on a once-daily dosing schedule, you generally have up to 12 hours to take the missed dose.
It's crucial to never double up on doses to make up for a missed one. Taking too much Amoxicillin at once can increase the risk of side effects and may not improve the effectiveness of the treatment. If you're unsure about what to do, it's always best to consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist for personalized advice.
Remember that consistency is key when taking antibiotics. Missed doses can potentially reduce the effectiveness of the treatment and may contribute to antibiotic resistance. Therefore, it's important to develop strategies to help you remember your doses, such as setting alarms on your phone or associating the medication with a daily routine like brushing your teeth.
Can I take Amoxicillin on an empty stomach?
Amoxicillin Powder can generally be taken with or without food, which provides flexibility in your dosing schedule. However, taking it on an empty stomach may help with absorption in some cases. If you experience stomach upset when taking Amoxicillin, consuming it with a meal or snack can help alleviate this side effect.
Here are some points to consider when deciding whether to take Amoxicillin on an empty stomach:
- Absorption: Some studies suggest that taking Amoxicillin on an empty stomach may lead to slightly better absorption. This means more of the drug enters your bloodstream, potentially increasing its effectiveness.
- Stomach sensitivity: If you have a sensitive stomach or have experienced nausea with antibiotics in the past, taking Amoxicillin with food can help reduce stomach irritation.
- Timing of meals: If you're supposed to take Amoxicillin multiple times a day, it may be more convenient to take it with meals to help you remember.
- Specific instructions: Always follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider or pharmacist. They may have reasons for recommending a particular way of taking the medication based on your individual health needs.
It's worth noting that while food doesn't significantly interfere with the absorption of Amoxicillin, certain foods and supplements can interact with antibiotics. For instance, dairy products can interfere with the absorption of some antibiotics (though this is less of a concern with Amoxicillin compared to other antibiotics like tetracyclines). If you're taking any supplements, especially those containing calcium, magnesium, or iron, it's best to separate these from your Amoxicillin dose by at least two hours.
Ultimately, the most important factor is consistency. Whether you choose to take Amoxicillin with food or on an empty stomach, try to do so consistently throughout your course of treatment. This helps maintain steady levels of the antibiotic in your system, which is crucial for effectively combating the infection.
What happens if you don't finish Amoxicillin?
Completing your full course of Amoxicillin Powder as prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial for several reasons. Failing to finish your antibiotic treatment can have serious consequences, both for your individual health and for public health at large.
Here's what can happen if you don't finish your course of Amoxicillin:
- Incomplete treatment of the infection: Even if you start feeling better, the infection may not be completely eradicated. Stopping the antibiotic prematurely can allow the remaining bacteria to multiply, potentially leading to a recurrence of the infection.
- Development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria: When you don't finish your antibiotic course, you may kill off the most susceptible bacteria while leaving behind the more resistant ones. These surviving bacteria can multiply and potentially become resistant to Amoxicillin and other antibiotics, making future infections harder to treat.
- Spread of infection: If your infection isn't fully treated, you may remain contagious for longer, potentially spreading the infection to others.
- Prolonged illness: Your symptoms may return, leading to a longer overall duration of illness and potentially more severe symptoms.
- Need for stronger antibiotics: If your infection recurs or worsens due to incomplete treatment, you may need a stronger or different antibiotic, which could have more side effects.
It's important to understand that the duration of your antibiotic treatment is carefully determined by healthcare professionals based on several factors, including the type and severity of your infection, your overall health, and the specific characteristics of the antibiotic. The prescribed duration is designed to ensure that the infection is completely cleared while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
If you're experiencing side effects or have concerns about your treatment, it's crucial to discuss these with your healthcare provider rather than stopping the medication on your own. They can provide guidance on managing side effects or potentially adjust your treatment if necessary.
In some cases, your healthcare provider might intentionally prescribe a shorter course of antibiotics. Recent research has suggested that shorter courses may be effective for certain infections while reducing the risk of side effects and antibiotic resistance. However, this decision should always be made by a healthcare professional based on the specific circumstances of your infection.
To ensure you complete your full course of Amoxicillin:
- Set reminders for each dose
- Keep the medication easily accessible but out of reach of children
- If you experience side effects, contact your healthcare provider for advice rather than stopping the medication
- Finish all the medication even if you feel better before the course is complete
By completing your full course of Amoxicillin Powder, you're not only ensuring the best outcome for your current infection but also contributing to the broader fight against antibiotic resistance, which is a significant global health concern.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Antibiotic Use and Resistance.
- World Health Organization. (2020). Antibiotic Resistance.
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Amoxicillin (Oral Route).
- National Health Service. (2021). Amoxicillin.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). Combating Antibiotic Resistance.
- American Academy of Family Physicians. (2019). Appropriate Use of Antibiotics.
- Infectious Diseases Society of America. (2021). Antibiotic Resistance.
- British Medical Journal. (2020). Antibiotic prescribing without documented indication in ambulatory care clinics.
- The Lancet. (2019). Antibiotic resistance: the need for global solutions.
- Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. (2018). The antibiotic course has had its day.

